What is the rebound hammer test?
The rebound hammer test is a non-destructive method of testing concrete and is used for the assessment of compressive strength, uniformity, and quality of elements of concrete.

With the help of suitable correlations between rebound index and compressive strength, the compressive strength of concrete is found. The test is mainly used to assess the uniformity of concrete in the structure and compare one concrete with another.
Rebound hammer test procedure
- A smooth, clean, and dry surface is selected for conducting the test. Rough surfaces should be avoided for the test.
- From any edge or shape discontinuity, the point of impact should be at least 20 mm away
- The rebound hammer should be held at right angles to the surface of the concrete member for taking measurements. On vertical surfaces, the test can be carried out horizontally, or vertically upwards or downwards on horizontal surfaces.
- The rebound hammer test is performed on a structural member around all sites of observation on all accessible sides.
- The concrete surface is cleaned before taking any measurement
- The apparatus must be kept at a place above the test specimen so that it can be allowed to drop freely
- The hammer is allowed to drop on the concrete surface, it rebounds back after it strikes the concrete surface and the raise of rebound is recorded
- Six readings of rebound indices are taken around each point of observation, and an average of these readings after deleting outliers as per IS: 8900-1978 becomes the rebound index for the point of observation.
- The value of compressive strength of concrete is obtained by doing a cube test of the test cube and the value of rebound and compressive strength is compared.
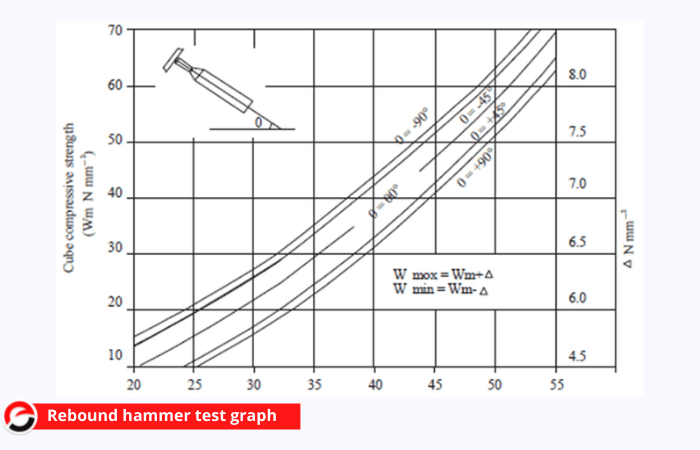
- The test is conducted in three positions vertical downward, vertical upward, and horizontally and graphs are drawn for each position.
Also read: Non-destructive testing methods of concrete
Rebound hammer test equipment
The apparatus required for the test are rebound hammer, anvil, test specimen. The hammer consists of a spring-controlled mass that slides on a plunger within a tubular housing.

For different applications the impact energy required for rebound hammers is different. The impact energy of 2.25 Nm for testing normal weight concrete, 0.75 Nm for light-weight concrete or small and impact sensitive parts of concrete, 2.25 Nm for testing mass concrete.
Rebound hammer test result
A suitable correlation between the rebound index and the compressive strength of concrete was established to provide a convenient and rapid indication of the compressive strength of concrete.
The rebound indices are indicative of the compressive strength of concrete to a limited depth from the surface. If the concrete in a particular member has internal micro cracking, flaws, or heterogeneity across the cross-section, the rebound hammer indices will not indicate the same.
The estimation of the strength of concrete by rebound hammer method cannot be held to be very accurate and the probable accuracy of prediction of concrete strength in a structure is ±25 percent.
Rebound hammer test result calculation
The result of the rebound hammer test is obtained by plotting a graph using the values obtained from the rebound hammer number and the compressive strength of the concrete.
The accuracy of the result may differ by ±25% to the compressive strength of the concrete.
|
SI |
Date | Test Point | Crushing value in N/mm2 | Rebound Number |
| 1 | ||||
| 2 | ||||
| 3 | ||||
| 4 | ||||
| 5 | ||||
| 6 | Average |
|
|
Average Rebound Number |
Quality of concrete |
|
>40 |
A very good hard layer |
|
30 to 40 |
Good layer |
|
20 to 30 |
Fair |
| ˂20 |
Poor concrete |
Compressive strength rebound hammer test graph
Application of rebound hammer test
The test is used to investigate the hardness of the concrete. It is used to test the fresh concrete as well as the in situ concrete after the final set. To find the exact location of poor quality and deteriorated concrete rebound hammer test is used. The uniformity of the concrete can also be assessed using this test.
Advantages of rebound hammer test
The advantages of the rebound hammer test are the apparatus is easy to use and also the equipment is inexpensive. It determines the surface’s homogeneity properties and is also employed in the restoration of historic monuments.
Disadvantages of rebound hammer test
The disadvantages are that the results obtained are based on a local point and it is not directly related to the strength and the deformation property of the surface. The spring and probe arrangement will require regular cleaning and maintenance and the flaws cannot be detected with accuracy.
Also Read: Complete Guide on Grades of Concrete
Factors affecting rebound hammer test
The factors affecting the rebound hammer tests are the types of aggregate used in the test, the type of cement used, the surface and moisture condition of the concrete, the curing and age of the concrete, and the carbonation of the concrete surface.

FAQs on Rebound Hammer Test
Rebound hammer test is code
IS 13311(Part 2):1992
The rebound hammer test is used for calculating the
compressive strength of concrete without any damage.
Rebound hammer test gives us an idea of the
uniformity of concrete
Why rebound hammer test is done?
It is done to measure the uniformity and relative quality of concrete in a structure or the manufacture of several similar precast members.


Leave a comment