What is retaining wall?
Retaining wall is constructed on ground to resist pressure of soil acting laterally due to change in ground elevation that would exceed soils angle of response with ground.Retaining wall is constructed to support soil on sloping surface. They are rigid walls used to retain soil from landscapes.
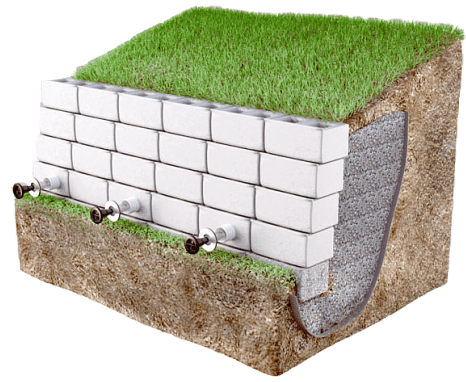
These are also more specifically used in hillside farming and roadway overpasses. Retaining wall helps to retains soil on backside of the wall. The walls which are constructed to retain water are called seawall it retains the water from front side.
The main accepts to be considered before designing a retaining wall are the required counteracting force that should be developed due to soil retained behind moving down slope due to gravity force.
Also Read: What are the different types of roads in India?
This downward force develops lateral earth pressure on the wall due to cohesive strength of soil retained on wall and angle on internal friction between wall and soil retained behind the wall.
Design Retaining Wall
There is wedge shape formation of soil behind the wall that extends the failure plan depending on the type of soil present on the site.
It can be calculated by finding frictional angle between soil and wall. As the sliding of wedge-shaped soil decrease it increases the setback of wall and lowers the soil lateral presser on the retaining walls.
The lateral earth pressure of soil is 0 at top due to less soil content above it but keeps on increases as we go depth into the soil. The maximum earth pressure is obtained at the lower depths of wall.
This earth pressure when exceeds beyond the counterforce of retaining wall it will push the wall forward or even some times overturning may be seen.
Hence while designing a retaining wall the maximum earth pressure should be considered and counterforce should be designed according to it
IS Code for Retaining Wall Design?
There are international building codes for design of retaining walls to safe guide it against overturning, sliding, foundation pressure and water pressure and it is designed with 1.5 safety factor against lateral sliding and overturning.
In construction of retaining wall we design steam of retaining wall, toe slab, heel slab and key. We also proved a weep hole or drainage system in the front face to slow down hydrostatic force on wall.
Also Read: What is roof and its types?
The toe slab is proved on the front side were as heel slab is proved on the rear face side of retaining wall. The backfill or earth soil is retained on the rear side of the retaining wall and angle of slope is considered the as angle between earths soil on rear wall and heel slab.
The soil or water above retaining wall can be said as surcharge. The lateral force or active pressure on retaining wall due to soil will be acting on steam were as passive earth pressure is acting below the toe slab on the key or base.
The weight of the wall will be acting downwards which is resisted by upward normal force of soil. There is a frictional force between base slab and soil at the bottom.
Drainage System in Retaining Wall
The hydro-static pressure on the retaining wall due to water or ground water. This total hydro-static pressure or up trust acts at one-third from bottom of wall in lengthwise direction of uniform heights’ proper drainage system is not created it causes increases in hydro-static pressure on the wall.
Hence proper drainage system behind the wall is necessary to limit the hydro-static pressure on the wall to its designed counter force to undergo overturning or pushing forces.
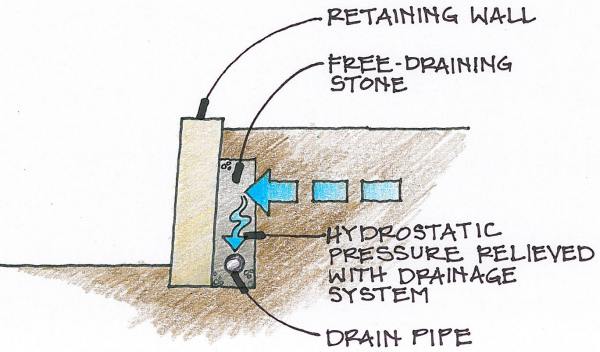
The provision of drainage system helps in stabilizing the soil behind the wall. There is self-draining retaining wall which are constructed by dry-stones.
Types of Retaining Wall
There are eight types of retaining walls as follows:
- Gravity retaining walls
- Reinforced retaining walls
- Brick masonry retaining wall
- Reinforced soil retaining wall
- Soil nailing
- Anchored earth walls
- Cantilevered retaining walls
- Sheet pile retaining walls
Let us discuss one by one.
Gravity retaining walls
Its main benefit is its huge weight structure which helps in holding the materials behind and achieving required stability against its failures. They have more thick sections constructed by concrete, stone and brick materials.
Also Read: Planning and Site Preparation for Concrete
Its geometry helps in maintaining stability of structure and they have the height up to 3m. It as long heel slab the toe slab and key at the bottom.
Reinforced retaining walls
Reinforced walls may be of concrete or masonry are built on spread foundations are of gravity structure. Which proved stability against overturning it is provided by its weight of the wall and reinforcement bars.

There are different types of walls main types of walls are as follows:
- Concrete cantilever retaining wall
- Counter fort retaining wall
- Precast concrete retaining wall
- Pre-stressed retaining wall
Reinforced soil retaining wall
These walls are made by stabilizing the earthen soil with reinforcing materials like: steel fibers and Geo textiles.
which may placed as layers with controlled granular fill or may be dispersed in the soil and compacted.

This category of walls uses earthen soil reinforced with reinforcing bars to have stable soil which acts as retaining system.
Soil Nailing
The walls built by soil nailing are constructed by introducing bars with tension called as passive bars in excavated areas. These bars are placed parallel to each another and inclined downwards.
These bars help in partial bending and shear stress. The friction between bars and soil creates the tensile force in the bars.
Anchored Retaining Walls
These walls are built by providing additional strength using cables or other anchored bars in the soil behind the retaining walls.

The bars are driven in the soil with boring and expanded at the end of the cable or by injecting pressurized concrete which forms a bed in the soil by holding the soil back.it is useful were heavy loads are applied.
Cantilevered Retaining Walls
These are made by steel reinforced, cast- in place concrete. These walls act as cantilevered beams taking cantilevered loads to footings.
Converting horizontal load of soil to the vertical pressure on ground below to foundations. It improves the strength by resisting heavy loads on the walls.

These walls have strong and rigid concrete footings below and it uses less construction materials than traditional gravity walls.
Sheet Pile Retaining Walls
These walls are generally used in soft soils and tight spaces. They are stabilized by mixing different types of fibres such as steel, polyvinyl, aluminium fibres, fibreglass or wood planks.
These fibres are mixed in different proportions and spread as sheets in top and bottom layers of the soil. 1/3 of fibres are driven in top ground surface and 2/3 are driven in bottom ground surface.

The loss in this wall is the fibres may alter due to environmental changes. Where as sheet pile walls which are provided with tie-back anchor are placed in the soil at a distance from face of the wall it is done usually by a rod or cable.
The anchors are mostly placed behind the potential failure plane in the soil.

