What Are Alluvial Soils?
Surface water deposits soils known as alluvial soils. They are present near rivers, stream terraces, floodplains, and deltas. The soil spreads out in the form of a triangle fan as a result of greater floods. Some soils are created through the extensive process of rock transformation. But these alluvial soils are developed differently.

Alluvial soil is one of the most effective types of soil for use in agriculture. It removes nutrients and other sediments from the flowing water through a filter. It can enhance the quality of the water out of the downstream.
Also Read: Different Types of Soil
How is Alluvial Soil Formed?
When materials like silt, gravel, and sand are carried downstream by rivers. They afterward dumped there. Then, alluvial soils are created. The water also deposits silt on the coastal plains due to wave erosion. Alluvial soil is eventually created when silt and humus are combined.
Alluvial Soil around the World
Except for Antarctica, all continents have alluvial soil. The floodplains of the Nile and Amazon rivers are one of the most fertile agricultural lands. Alluvial soil makes up a significant part of the soils in China, India, and the United States. Alluvial soil has a lot to offer, but it can also cause issues. In locations with alluvial soils, flooding is a significant risk. As a result, the soil is frequently quite erosive.

Alluvial soils can be challenging to manage. It may need extra attention to sustain its production. Alluvial soils can be found in the Rhine and Danube river floodplains in Europe. It can be found in the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Irrawaddy river deltas in Asia. It can be found throughout the Nile delta in Africa. Australian floodplains of the Murray-Darling river system contain alluvial soil.
Characteristics Of Alluvial Soil
Silt, sand, clay, gravel, and a sizable amount of organic materials make up alluvium. The alluvial soils have weak profiles since they are recent in origin. Floods deposit new layers over the previous one in a continuous manner. Alluvial soils have a distinctive layered appearance. Many floodplains exhibit this stacking or stratification, process. Due to an incomplete soil profile, alluvial soils are considered immature soil. The following are the primary attributes of alluvial soil:
- Alluvial soil has a sizeable amount of organic elements. Adding up, alluvial soil also contains silt, sand, clay, and gravel.
- The alluvial soils have shallow profiles. They are very young in comparison to other soil types.
- Alluvial soils have a distinctive layered appearance. Because flooding often deposits new layers on top of the older ones.
- The process of stratification results in the production of layers. It is evident in many floodplains to form alluvial soils.
- Alluvial soils are categorized as immature soils. The soil profile is still developing.
- Alluvial soil has a loamy texture. It is mostly characterized by a blend of sandy and clayey components.
- Alluvial soil was created as a result of river erosion, transit, and deposition. This process explains why this type of soil has a variety of textures.
- The soil is exceptionally porous. Alluvial soil has excellent drainage due to its roughness.
- Water from the river or stream often seeps into it. It causes alluvial soil to replenish. This is making it one of the most productive soils for crop development.
- Alluvial soils typically contain little nitrogen. But this soil does contain considerable amounts of alkalis, potash, and phosphoric acid.
- A considerable part of the world’s tin ore supply comes from alluvial soil.
- Alluvial soil has a ratio of iron oxide to lime. It always varies within a wide range of acceptable values.
- Alluvial soil deposits also contain gold, platinum, and precious stones. These deposits may be found in specific locations.
Chemical Properties Of Alluvial Soil
The main chemical properties of alluvial soil are mentioned below:
- The amount of nitrogen is often little.
- Potassium, phosphoric acid, and alkalies are present in an adequate ratio.
- There is a wide range in the ratio of iron oxide to lime.
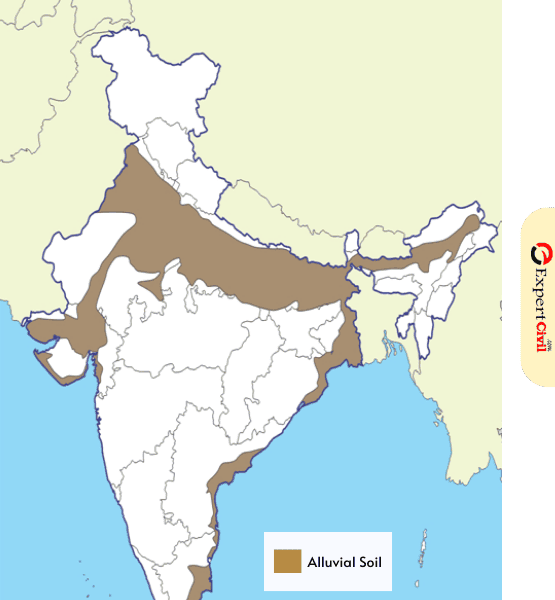
Distribution of Alluvial Soil In India
The Indo-Gangetic-Brahmaputra plains are covered in alluvial soils. There are only a few places where alluvial soils are present. The area begins as a layer of desert sand covers the top layer. Alluvial soils may find in “deltaic alluvium” in the Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, and Cauvery deltas (coastal alluvium).
Crops in Alluvial Soil
Alluvial soil is one of the best soils used for cropping. Alluvial soils help to grow plants. This soil contains all essential nutrients. That’s why it has a significant role in agriculture. The following crops are most of the time cultivated in alluvial soils:
- Alluvial soil produces excellent crops. The major crops are; rice, wheat, sugarcane, tobacco, cotton, jute, maize, oilseeds, vegetables, and fruits.
- Alluvial soil is best suited for irrigation. It responds well to canal and well/tube-well irrigation.
- Alluvial soils are mostly flat and regular soils that are suitable for agriculture.
Types Of Alluvial Soil
1. Khadar
Khaddar alluvial soil is defined as a fresher and younger alluvium soil. The soil deposits are found on flood plains. Since this soil is regenerated each year, it is more fertile than the soil in Bhangar. It is drier and leached, less calcareous, and carbonaceous. Hence Khaddar alluvial soil is the most fruitful soil of the Ganges (less kankary).
The Khadar is the soil present along the rivers. It is made up of more recent alluvium. Almost every year, the banks are flooded. And each flood deposits a fresh layer of alluvium. They are sandy clays and loams. Almost every year, a new layer of alluvium is added by river flooding.
2. Bhangar
The soil of Bhangar is older alluvial soil. Bhangar soil makes up a significant section of the Northern Indian Plains. The soil has a terrace-like appearance. It is not as productive as the soil in Khadar.
The earlier alluvium along the river beds is recognized as the Bhangar. It has formed terraces that are higher than flood plain. It has a more clay-like composition. It is typically very dark in color. “Kankar” beds of lime nodules can be found a few metres below the terrace of the Bhangar.
Conclusion:
Thus, alluvial soil can be found in deltas, floodplains, and close to riverbanks. It is viewed as a vital type of soil. Alluvial soil always plays an important role in our environment. Alluvial soils preserve the health of our ecosystem.
Alluvial soil has a variety of its types. It has different textures according to its deposition layer. Alluvial soil has a significant role in agriculture. It is considered a ‘complete soil’ for the cultivation of crops.
Also Read: Different Types of soil Excavation Tools and Machines In Construction


Leave a comment