Rise and fall is the method of surveying to solve the levelling to find out the difference in elevation and elevation of two points. In this method
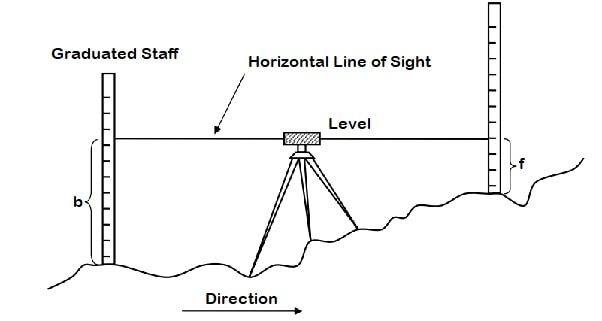
Like we need to calculate the difference in elevation of the staff of two points. The two stations points where the staff readings are taken, we know the RL of ground of one station and we have to find the RL of another.
What is Back Sight?
Backsight is a first reading of a staff (levelling rod) which remains unchanged when the levelling apparatus is taken to another or new point after the levelling instrument is set up and levelled on the first point. And simply it can be defined as the backward reading of the previous station point. It is taken on the known reduced level or benchmark.
Also Read: Traverse Surveying – Definition, Types, Methods, Checks
What is Intersight?
All the reading which is taken between backsight and foresight is called inter-sight.
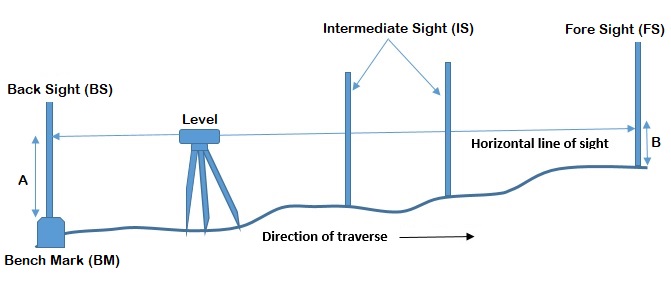
What is Fore Sight?
Foresight is the reading of the staff or levelling rod which is taken in the forward direction of the leveling process or the staff reading which is to be determined and it is a last reading of the whole surveying process. It is considered as negative and deducted from the Height of the Instrument to determine RL of the point.
What is a Benchmark?
Benchmark is considered as the fixed point of known elevation point through which the reduced level of the other point is determined.
It is arbitrary or permanent reading through which the survey works are done and calculation of the reduced level is done. For the GTS surveys work, the surveyor uses an identified or permanent benchmark to calculate the elevation of the points.
Also Read: Reconnaissance Survey in Civil Engineering
Rise and Fall Method Formula
Determine the rise or fall using:
B.S-I.S or I.S-F.S
Where;
- B.S= back sight
- F.S= fore sight
- I.S= intermediate sight
If,
B.S-F.S=+ve (Rise) & B.S-F.S=-ve (Fall)
Determining new R.L
New R.L= Old R.L-fall = Old R.L+rise
Arithmetic checking
∑B.S – ∑F.S = ∑Rise – ∑Fall = Last R.L – First R.L
Advantages of Rise and Fall Method
- The advantage of the Rise and fall method is that it gives more accuracy in the reading and it includes many steps.
- This method is quite complicated and is not easy to use.
- It is used where the change point is more and the reduced level takes more time. Imagination or visualization is required for the nature of the ground.
- A complete check is done for all the readings.
Let us discuss this with few real calculations related to the Rise and Fall method.
Example #1
The following staff readings were obtained during a leveling work with the instrument being shifted after the 4th, 7th and 10th. Readings: 2.305, 0.940, 0.865, 1.325, 2.905, 1.185, 1.205, 2.015, 1.365, 0.985 and 1.785. Find the reduced levels of the remaining points if the RL of the second turning point is 200.00
| Points | B.S | I.S | F.S | Rise | Fall | R.L | Remarks |
| 1 | 2.305 | 198.635 | |||||
| 2 | 0.940 | 1.365 | 200 | RL=200 | |||
| 3 | 0.865 | 0.075 | 200.075 | ||||
| 4 | 2.905 | 1.325 | 0.46 | 199.615 | C.P | ||
| 5 | 1.185 | 1.72 | 201.335 | ||||
| 6 | 2.015 | 1.205 | 0.02 | 201.315 | C.P | ||
| 7 | 1.365 | 0.65 | 201.965 | ||||
| 8 | 0.985 | 0.38 | 202.345 | ||||
| 9 | 1.785 | 0.80 | 201.545 | Endpoint | |||
| Total | ∑B.S=7.225 | ∑F.S=4.315 | ∑Rise=0.53 | ∑Fall=1.6 |
Arithmetic Check :
∑B.S –∑F.S = ∑Rise – ∑Fall = Last R.L – First R.L
= 7.225 – 4.315 =4.19 – 1.28 = 201.545 – 198.635
= 2.91=2.91=2.91
Hence checked.
Example #2
Eight readings were taken with a level in sequence as follows: 1.585, 1.315, 2.305, 1.225, 1.325, 1.065, 1.815, and 2.325. The level was shifted after the third and sixth readings. The second change point was a benchmark of elevation 175.975. Find the reduced levels of the remaining stations. Use the rise and fall method.
| Points | B.S | I.S | F.S | Rise | Fall | R.L | Remarks |
| 1 | 1.585 | 176.67 | B.M1 | ||||
| 2 | 1.315 | 0.27 | 176.94 | ||||
| 3 | 1.225 | 2.305 | 0.99 | 175.95 | B.M2-175.95 | ||
| 4 | 1.325 | 0.1 | 175.85 | ||||
| 5 | 1.815 | 1.065 | 0.26 | 176.11 | BM3 | ||
| 6 | 2.325 | 0.51 | 175.6 | ||||
| Total | ∑B.S=4.625 | ∑F.S=5.695 | ∑Rise=0.53 | ∑Fall=1.6 |
Arithmetic Check:
∑B.S –∑F.S = ∑Rise – ∑Fall = Last R.L – First R.L
= 4.625 – 5.695= 0.53-1.6 = 175.6- 176.67
= -1.07 = -1.07 = -1.07
Hence checked.
Also Read: Types of Chains and Tapes in Civil Surveying Engineering


[…] Civil engineers use formulas to design and analyze structures such as bridges, buildings, rise and fall, and roads. They also use formulas to calculate things like load capacity and material strength. […]