Definition of road margin
Lines, patterns, and phrases, with the exception of road signs, are applied or fastened to the carriageway or kerbs, or to objects inside or adjacent to the highway, for the purpose of managing, warning, guiding, and informing road users.
What are Road Margins?
The different cross-sectional parts of the road, excluding the carriageway or pavement width, are referred to as road margins. Also Read: Complete Guide on Road StudsDifferent types of road margin in highway
The following are the elements of the road margins.- Shoulder
- Footpath
- Cycle-track
- Frontage Path
- Drive-ways
- Lay Byes
- Parking Lanes
- Side Slopes
- Guide Rails
What is Shoulder in Road?
Except for carriage ways, shoulders are the parts of the formation width. In other terms, the non-surfaced portion of the pavement is known as the shoulder. It’s an emergency stopping lane on the side of a road or highway, on the right in countries where people drive on the right, and on the left in countries where people drive on the left. Along the road’s edge, there is a shoulder of the road.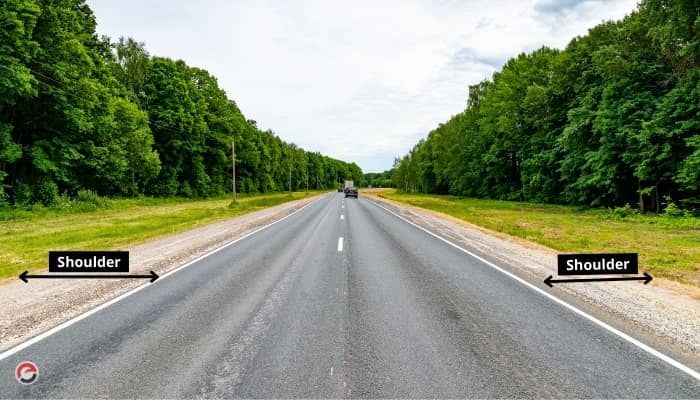 They are utilised by vehicular traffic as emergency lanes or, on occasion, as service lanes for the repair of unanticipated difficulties. For two-lane country roads, the IRC recommends a minimum shoulder width of 2.5 metres. A width of 4.6 metres is recommended to accommodate a truck without obstructing the neighboring lane.
The major purposes or objectives of the road shoulder are
They are utilised by vehicular traffic as emergency lanes or, on occasion, as service lanes for the repair of unanticipated difficulties. For two-lane country roads, the IRC recommends a minimum shoulder width of 2.5 metres. A width of 4.6 metres is recommended to accommodate a truck without obstructing the neighboring lane.
The major purposes or objectives of the road shoulder are
- To accommodate stopped vehicles
- To provide structural stability and support to the edges of the flexible pavements, particularly to the granular pavement layers.
- To serve as an emergency lane for vehicles
What is a Road Footpath?
A road footpath is a sort of roadway designed just for pedestrians and not for other types of transportation such as cars, bicycles, or horses. Where there is a high volume of pedestrian traffic, footpaths are required. They can be found in a range of locations, including city centres, farms, and mountain ridges. Alleyways, lanes, steps, and other names for urban walkways include alleys, lanes, and steps. Pedestrians use footpaths, especially in urban areas. 1.5m should be the minimum width. The footpath should be provided with a surface as smooth as or even smoother than the adjacent traffic lane so as to induce the pedestrians to keep on to the footpath. The cross fall of the footpath maybe 2.5 to 3.0 percent.
Pedestrians use footpaths, especially in urban areas. 1.5m should be the minimum width. The footpath should be provided with a surface as smooth as or even smoother than the adjacent traffic lane so as to induce the pedestrians to keep on to the footpath. The cross fall of the footpath maybe 2.5 to 3.0 percent.
Cycle-track
A cycle track, also known as a separated bike lane or a protected bike lane, is a private bikeway with aspects of both a separated path and an on-road bike lane. They are available in urban locations where there is a large number of cycle traffic. A minimum of 2 m in width is necessary.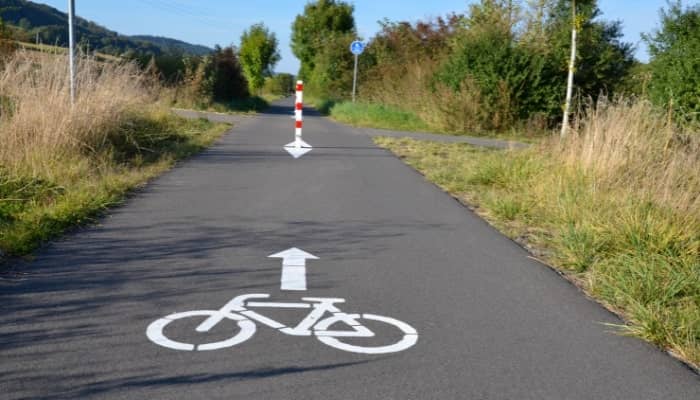
Frontage Path or Road
A frontage road (sometimes called an access road, outer road, service road, feeder road, or parallel road) is a local road that runs beside a higher-speed, limited-access highway. Access to private driveways, shops, houses, factories, or farmland is frequently provided via a frontage road. Local-express lanes refer to parallel high-speed roadways that are given as part of a main highway.
Driveways Road
Driveways are offered to reach establishments such as gas stations and service centres. Driveways should be as narrow as possible since they obstruct pedestrian traffic traveling along footpaths. Driveways should be properly designed and located, fairly away from an intersection. The radius of the drive way curve should be kept as large as possible, but the width of the drive should be minimised to reduce the crossing distance for the pedestrians.
Lay By Road
Lay By are paved areas installed along the sides of the roads to offer a place for vehicles to stop. They should normally be of 3 m width and at least 30 m length with 15 m end tapers on both sides.
What is Parking Lanes on the highway?
For side parking, parking lanes are provided in urban lanes. Because side parking is dangerous, parallel parking is preferred. In the case of parallel parking, parking lanes should be at least 3 metres wide. In addition, in parallel parking, the clearance available between the parked vehicles and the edge of the adjacent lane is greater than in angle parking.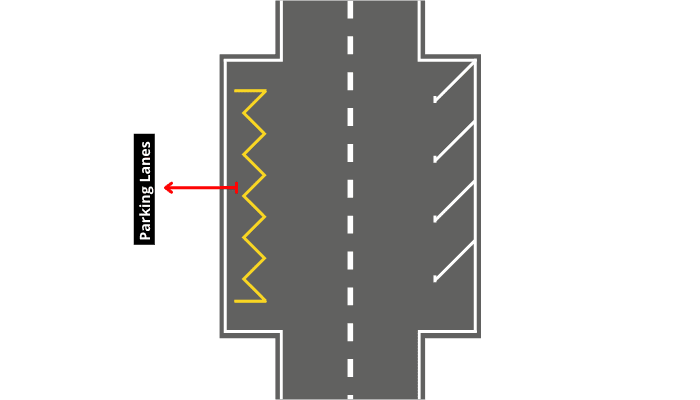
Side Slopes
For the stability of the pavements, suitable, flatter/gentle side slopes are required for filling or cutting. If at all possible, landscaping should be installed to give them a more pleasant and appealing aspect while also increasing their stability. Must Read: What is Slope Failure and Its Different TypesGuide Rails
Guide rails are provided at the edge of the shoulder when the road is constructed on a hill so that vehicles are prevented from running off the embankment, especially when the height of the hill exceeds 3m. For the driver’s psychological as well as physical protection, guide rails are put on the highways on filling, often on the slopes, on the outer margins.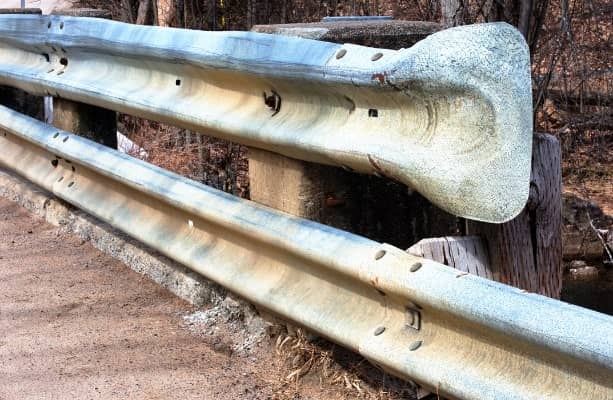 Also Read: What are the different types of Roads?
Also Read: What are the different types of Roads?
Road Terminology
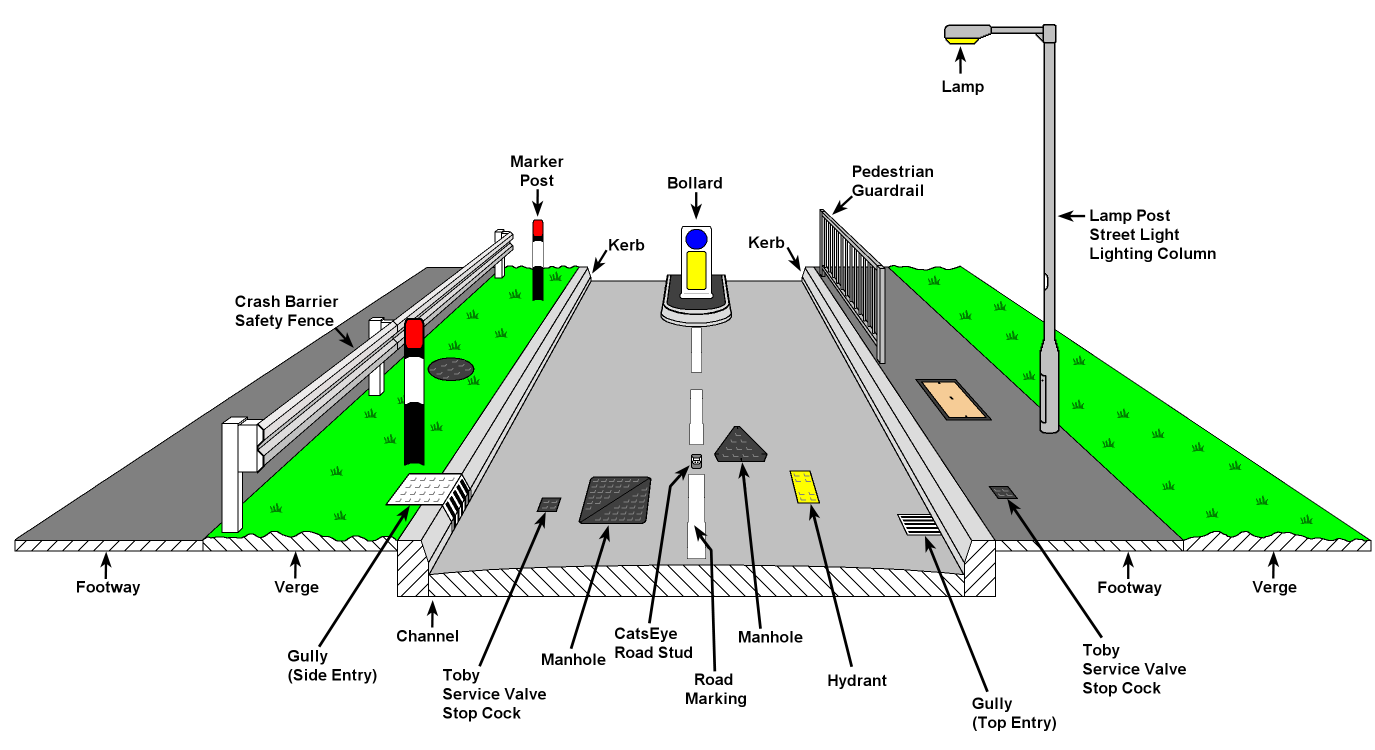
Source: ayrshireroadsalliance.org
Formation Width of Road as per IRC
The formation width of the road is the sum of widths of pavement or carriageway including separators if any and the shoulders.| # | Road Classification | Roadway Width in metre (m) | |
| Plain and rolling terrain | Mountainous and steep terrain | ||
| 1 | National and State Highways | ||
| A. Single Lane | 12 | 6.25 | |
| B. Two Lane | 12 | 8.80 | |
| 2 | Major District Roads | ||
| A. Single Lane | 9.0 | 4.75 | |
| B. Two Lane | 9.0 | – | |
|
3 |
Other District Roads | ||
| A. Single Lane | 7.5 | 4.75 | |
| B. Two Lane | 9.0 | – | |
| 4 | Village roads, single lane | 7.5 | 4.00 |
Right of Way on Road
It is the area of land required for the road, along its alignment. The width of the acquired land for the right of way is known as land width.|
Road Classification |
ROW on Road (m) |
||
|
Plain and Rolling terrain |
Mountainous and Steep Terrain |
||
| Open Areas | National or State Highway |
45 |
24 |
| Major District Road |
25 |
18 |
|
| Other District Road |
15 |
15 |
|
| Village Road |
12 |
9 |
|
| Built-up areas | National or State Highway |
30 |
20 |
| Major District Road |
20 |
15 |
|
| Other District Road |
15 |
12 |
|
| Village Road |
10 |
9 |
|


Leave a comment