What is precast concrete?
Precast concrete is defined as concrete which is cast and cured at different locations and used at other locations. This concrete has good quality control. It helps in fast construction on site. It is high-quality concrete. This type of concrete has the higher industrialized quality and also it is less affected by the weather. Also, it has unlimited opportunities for architectural appearance.

Concrete is heavy typically about 150 pounds per cubic foot so concrete elements don’t have to be very big before moving them becomes unrealistic. Some decorative contractors, such as those that precast concrete countertops, stretch the boundaries on what’s too big or heavy to move, developing special rigs to transport massive pieces of their concrete work. Other times, it’s just simpler to cast the concrete in place as the precast advantages are outweighed by conveniences, such as concrete slabs and floors.
Types of precast concrete Elements
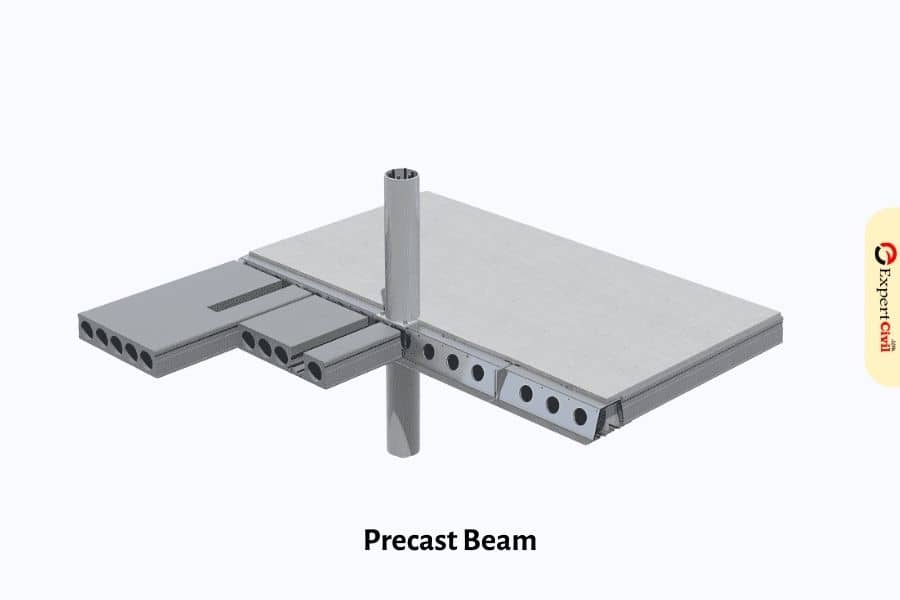
Precast Beams
These are the beams which are already constructed in the industry with precast concrete and used as a ready-made beams on the structure. Its cross-section depends upon the place or location within a structure where it has to be placed. These beams are of four types.
- Rectangular beam – It is also represented as RB. Generally, beam width= 12” to 16”. Span may be up to 50’. These beams can be designated as – 16RB24 (where 16 = width of the beam and 24 = depth of the beam in inches).
- L and IT beams – IT means Inverted Tee Beams. These beams are used to support slabs, walls etc. The standard width of these beams is 12”. Depth of these beams may be 20”, 28”, 34”, 44”, 52” and 60”.
- Double Tee beams – These beams are a combination of slabs and beams. It has a slab up to 100′-0”. Standard width of such beams are 8’-0”. Depths of these beams are 12”,18”, 24”, and 32”.
- Single Tee beams – These beams are also the combination of slab and beam. It has a span of up to 120’-0”. Width of such beams are 8’-0”. The depths of such beams are 36” and 48”. These beams are designated as 8ST36+2 (where 8 = width in feet, 36 = depth in inches, +2 = 2” tapping).
Precast floor slabs
Precast members or a precast slab is built outside the building site to permit better and controlled conditions that match up to industry guidelines. This likewise accelerates the interaction where if we construct a structure nearby where we need to trust the process of precasting where we need to wait for concrete to set and its curing.
However, the precast elements are as of now exposed to every one of these in the production line and are recently purchased and collected at the site.
These slabs are of two types:
- Flat slabs – Generally these slabs have thicknesses of 4”, 6” and 8”. These slabs are of span 25’-0”. It also have standard panel 4’-0”. These slabs are designated as FS4 which means a flat slab of a thickness of 4 inches.
- Hollow core slab – These slabs have thickness of 4”, 6”, 8”, 10” and 12”. It has a span up to 40’-0”. Panel width = 4’-0”. These beams are designated as : 4HC6 (where 4 = panel width in feet , HC = Hollow core, 6 = slab thickness in inches).
Precast concrete walls
Precast concrete walls are built by projecting cement in a reusable wall shape or structure, which is relieved in a controlled climate, moved to the building site, and lifted into place. The principal development of precast walls is to accelerate the development cycle.

Precast wall panels are in the standard form of width 8’-0”. It can be flat also may have some architectural features such as windows and doors openings etc.
Types of Precast Concrete Walls:
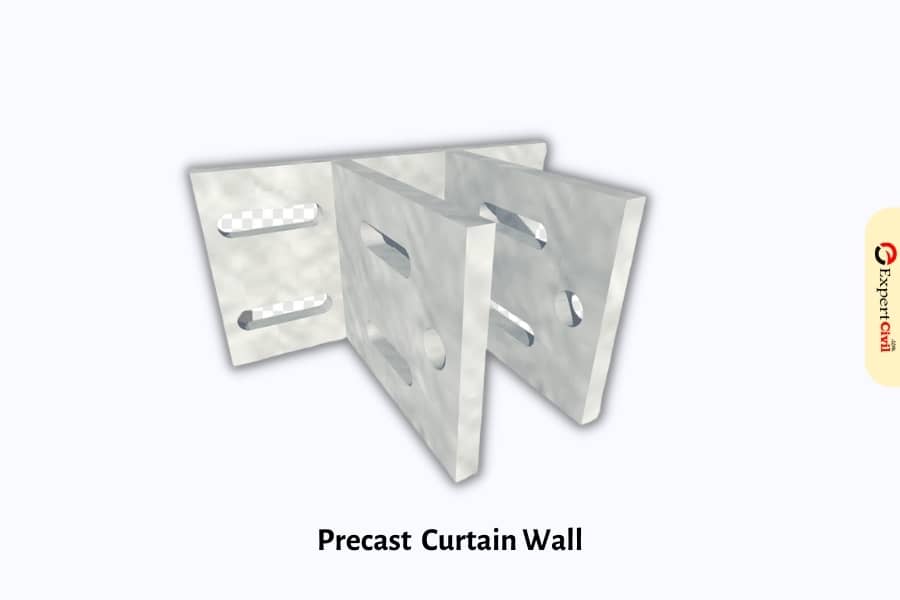
1. Cladding or Curtain Walls
The most popular precast wall for external walls is the cladding or curtain wall. They are non-load-holding walls designed to fight the wind and enclose the space. This particular style of the precast wall includes section coverings, spandrels, mullions, and window separator components.

2. Load-bearing Wall
The quality or reliability of the structure will be negatively affected if load-bearing wall units are removed or destroyed since they oppose and interchange loads from various components.

3. Shear Walls
Shear walls are used in conjunction with the floor development’s stomach action to provide a parallel load countering framework. Precast shear dividers’ feasibility typically depends on platform interconnections.
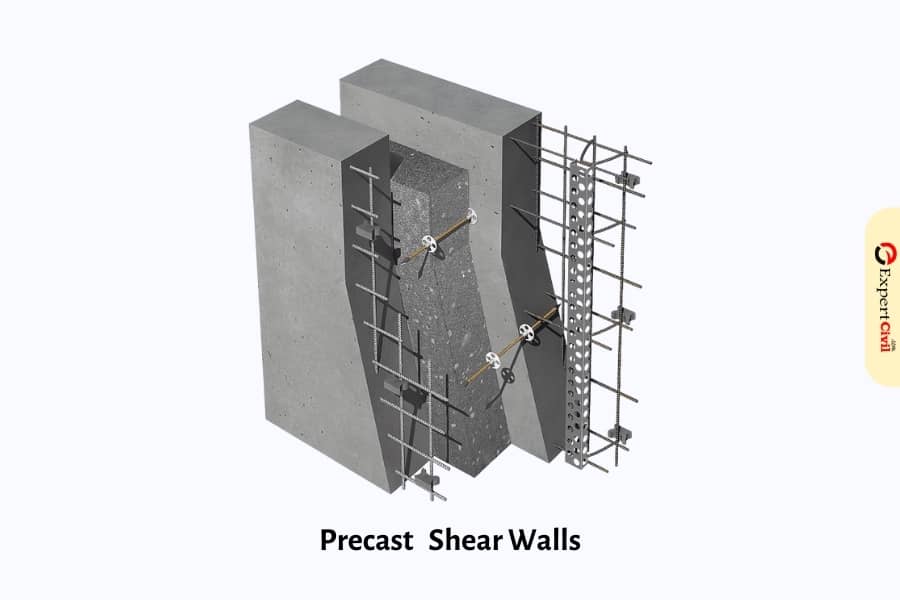
Types of Connections in Precast Concrete Walls
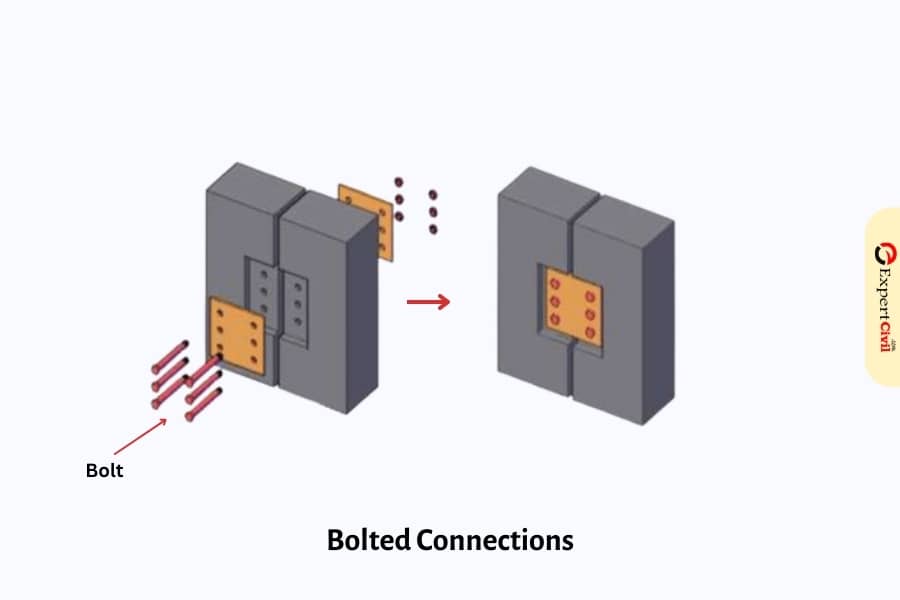
1. Bolted Connections
The bolted connections are a streamlined and quickest strategy for erection activity. The last arrangement and change can be made later without tying up crane time. The bolting order should be as per the production drawings, utilizing material determined by the creator.
2. Welded Connections
The welded connections are the most well-known and normal association utilized in the creation of precast cement. These associations are fundamentally proficient and change effectively to fluctuating field conditions.

The connections are normally made by putting a loose plate between two underlying steel plates that are implanted both in the cast set up or the precast concrete panel and welded together.
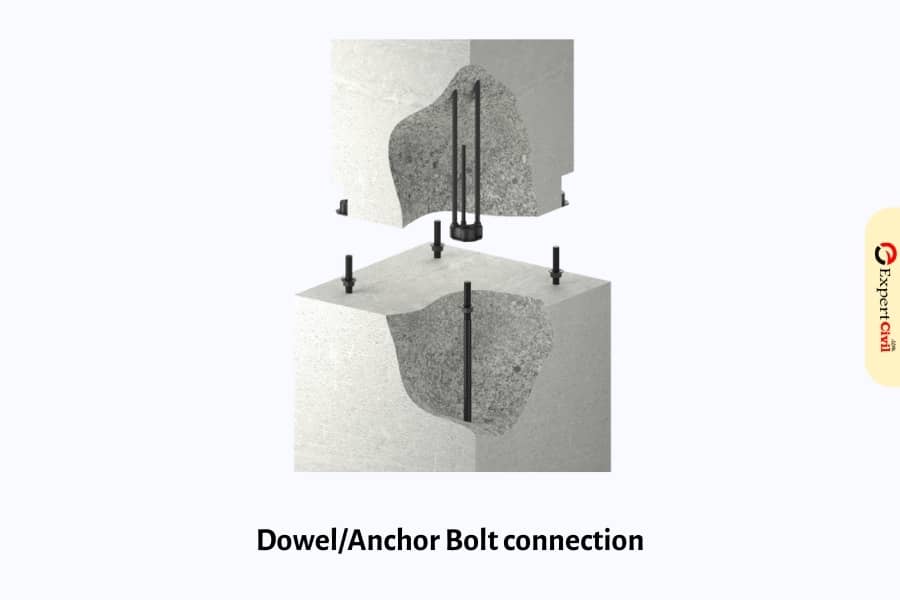
3. Dowel/Anchor Bolt connections
In a dowel connection, the strength of dowels in pressure or shear relies upon dowel width, implanted length, and the bond created. The threaded anchor bolts and rebar anchor dowels that protrude from the establishment are the basic first association with precast individuals.
Precast Stairs
Stairs are constructed according to the standard size and size required at the site. After complete curing, these stairs are moved to the place of construction where they are needed.
Precast concrete steps are cost-effective and quality items that rush to introduce on the building site. The precast flight of stairs eliminates the requirement for any brief metal or wooden step arrangement and kills the requirement for complicated formwork and setting of the casting design whenever made cast-in-situ.

A precast of stairs is an expense effective and safe. It is a safe and heatproof arrangement. Precast steps range from individual stairs to straight monobloc units with arrivals. Flights and arrivals of the straight step can be given a role as isolated components or consolidated in one piece. There might be differential levels at floors and half-arrivals in the last arrangement, requiring a complete finishing or other arrangements. Elematic offers a wide range of different staircase moulds.
Precast Column
These columns are constructed according to the there need at the site and after proper curing, they are moved and placed at their place in the construction.
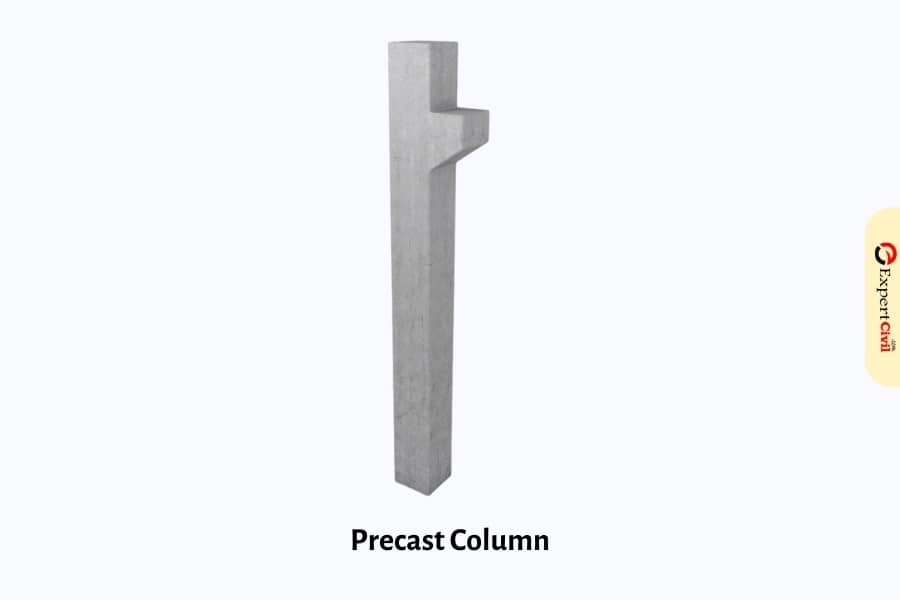

Foundation connection might be through a base plate associated with the section or by supporting bars projecting from the finish of the segment passing into sleeves that are in this manner loaded up with grout. On the other hand, a column might be set into a preformed opening in a foundation block and grouted into position.
Also Read: 3-Point Bend Test of Concrete and Beam
Advantages of Precast Concrete
There are many advantages of precast concrete. Some of these are mentioned below:
- It has a rapid speed of erection
- It has good quality control
- It gives a high-quality concrete
- It gets less affected by the weather
- It helps in rapid construction on site
- Entire structure can be of precast materials such as precast beams, precast columns, precast slabs, precast floors, etc.
- Pre-stressing can be easily done which can reduce the size and number of structural members
- It has good industrialized quality
- It has a low maintenance cost
- Also, it is economic in nature and gives an aesthetic appearance to the structure
- These structures are durable in nature
- Precast concrete construction also helps in the reduction of air pollution, noise and debris.
- It can be converted into desirable shape and sizes.
- There is not necessary to provide joints.
Disadvantages of Precast Concrete
There are some disadvantages to precast concrete.
- Some members are very heavy in weight.
- Making connections between the joints sometimes may cause difficulty and get complicated and expensive
- Heavy cranes are required to lift the members
- It has constructed with a very small margin of error
- There is a need for repetition of forms which can affect the design of the building
- If not properly handled it may cause huge damage.
Also Read: What is Concrete Crazing – Causes and Treatment
Precast concrete manufacturing process
There are some factors which are considered for the manufacturing of precast materials such as:
Procurement of concrete materials: It is the process in which concrete material is selected, ordered or bought for the required construction. This process also involves identifying the suppliers, negotiating prices, terms and conditions, awarding contracts, etc. In simple words, it is the purchasing process of concrete materials.
Storage and handling: The storage of cement should be in the waterproof shed and kept dry. It should be carried safely from one place to another. There shouldn’t be any leakage in the storage shed. The roof of the storage should be waterproof so that rainwater penetration should be controlled.
Batching of concrete components: It is the process in which the materials used for the construction of concrete components are measured on the basis of volume or kilograms to prepare the concrete mix. It also involves the workability of concrete by reducing the bleeding in concrete.
Laying of concrete in required formwork with or without reinforcement as per design: In this process, concrete is filled in the mould or form to get the required shape for the construction. In case of reinforcement, the reinforcement is properly tied up according to the need and set up inside the mould. After this setup, the concrete is filled up inside the mould and treated in a controlled environment to get the required result. In case where reinforcement is not required then the concrete is directly filled into the mould and treated accordingly.
Concrete compaction: It is the process in which the extra air is expelled out from the freshly prepared concrete. This process helps in increasing the density of the concrete. The load is provided on the freshly prepared concrete, which makes the aggregate closely packed and increases the density of the concrete.
Curing of concrete: It is the process in which concrete is placed under a closed chamber and superheated steam at a very high temperature and high pressure is applied to the concrete. This process is used in practice for the curing of precast concrete components.
Finishing of concrete: The main purpose of this process is to remove small surface imperfections from the surface of the concrete and make it smooth.
Transporting the inserted member on site: When concrete is properly cured and finished with the required needs then it is ready for use at its place on site. It is transported from the industry to the site and directly used at its placed where it needs to be. The transportation of the concrete is done by heavy vehicles or large vehicles which can carry these materials.
Uses of precast concrete
- Precast concrete is widely used nowadays. It is mostly used in low-rise and mid-rise structures.
- Due to its lightweight, it is easy to transport from one place to another.
- Also, the components of precast materials can be reused.
- It also gives uniformity to the structure.
- Using of precast materials on the construction site is a time-saving option in comparison to the in-situ preparation of concrete.
- It gives high-quality products.
- Installation of these components is very easy and time-saving.
- This type of concrete also reduced air pollution and noise pollution at the construction site.
- These are lightweight structures that can be easily moved from one place to another.
- The high-quality finishing to this concrete means that it can be left in the air without treatment or painting and it can also be exposed to the sun without covering
- It gives the maximum thermal mass benefits to the structure.
- It also contributes to green environment management practices
Also Read: 9 Best Methods of Transportation of concrete


Pre-cast concrete serves as a flexible construction material, with concrete elements being formed in a controlled setting and then transported to the construction site. It provides robust connections, longevity, and rapid construction. Common applications involve beams, slabs, and panels. Although it is cost-efficient and minimizes on-site labor, there are drawbacks related to transportation logistics. The production process ensures consistent, high-quality components for a variety of structures.