Manufacturing of Cement By Dry and Wet Process
Manufacturing of Cement
In the manufacturing of cement, the following three important and distinct operations occur:
- Mixing of Raw materials.
- Burning
- Grinding
The process, by which cement is manufactured, depends upon the technique adopted in the mixing of raw materials. Therefore, on the basis of mixing the raw materials, the processes may be classified as:-
- WET PROCESS
- DRY PROCESS
Out of this wet process is generally used.
The Raw material, which is used for manufacturing of cement, contains the following materials:
- CALCAREOUS (i.e. chalk consists of limestone.)
- ARGILLACEOUS (i.e. clay consists of silicates of alumina.)
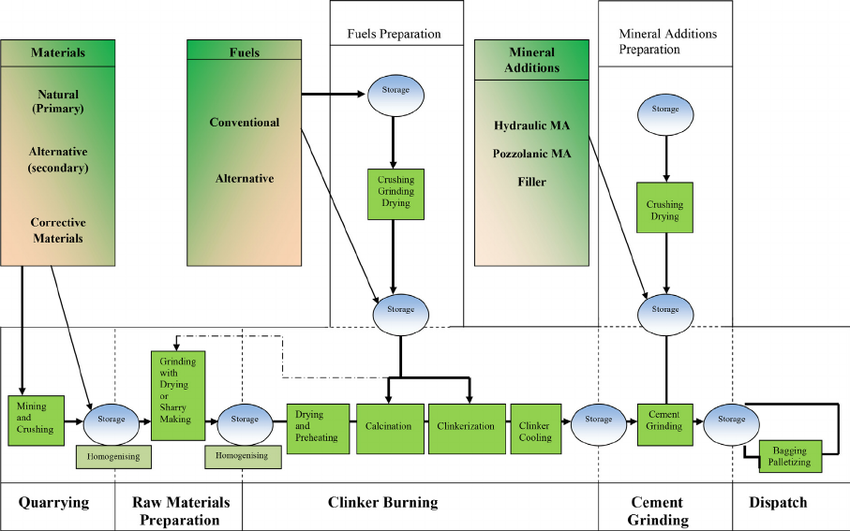
Here is the manufacturing of cement by wet process
WET PROCESS
When the raw materials are soft, then the wet process is preferable to be used. The cement is manufactured by the following procedure:-
Mixing of Raw Materials:
- In the wet process, there are two raw materials e. calcareous and argillaceous. Initially, Calcareous materials are crushed using crushers and argillaceous material is washed With water in the container.
- After crossing the line stones are stored in silos similarly after washing the clay is stored in basins.
- The crushed materials from different silos and basins are drawn in correct proportions in a channel called wet grinding mills. Both the materials are intimately mixed in the presence of water and to form a fine thin paste known as slurry
- Slurry is then stored in another silo may be called as slurry silo where it is constantly stirred. The composition of raw materials is checked again and, if required, corrected by adding clay or chalk materials as desires.
Burning: In this operation, the slurry is directly fed into a long inclined steel cylinder called a Rotary kiln. In this kiln there are 3 different zones shown in fig. below
Cement Manufacturing Process Flow Chart
(i) Drying Zones: In the wet process, the drying zone is comparatively larger than the dry process. It is because the raw material in slurry form is directly fed into the kiln which has more amount of water. As shown in the figure it is the upper portion of the kiln. In this zone, water is evaporated at a temperature of 100-400°C.
(ii) Formations of modules: As the slurry gradually descends in the kiln, the carbon dioxide from the slurry evaporates and small lumps formed which may be called modules.
(iii) Burning Zone:- The modules enter this zone where temperatures are kept about 1400-1500° C. The modules are converted into dark greenish balls and the product obtained in the kiln, known as clinker, is of varying size 5 to 20 mm. The clinkers are very hot when coming out of this zone.
(iv) Cooling of Clinkers:- As shown in the figure another rotary kiln is provided in an opposite direction which is also inclined. It is used to cool down the clinkers up to about 90°C.
Grinding: The cooled clinkers are finely ground in ball mills or tube mills.
Also, the gypsum is added during grinding about 2-4%. The gypsum acts as a retarder and so allows the cement to mix with sand or aggregate and to be placed in position. i.e. it increases the initial setting time of cement.
Storage and Packing: As cement comes out from grinding mills, it is collected in a hopper and taken in bucket elevator for storage in silos.
The cement from silos is packed by machines in bags. Each bag of cement contains 50 kg or 0.035 m3 of cement.
Now let’s know the manufacturing of cement by the dry process
DRY PROCESS
When the available raw materials are quite hard, then this process is used. The cement by this process can be prepared by using the following operations:-
- Mixing of raw materials
- Burning and Grinding
Mixing of Raw Materials: The raw materials i.e. argillaceous and calcareous materials undergo the following stages:-
- Crushing: The raw materials, first of all, are broken into crushers into small fragments that vary in size.
- Drying: The crushed materials are dried by heating at a sufficiently high temperature. It may be done in drying kilns.
- Reduction of size: The drying materials are then ground by using ball mills and tube mills to reduce the size of materials to find powder.
- Mixing in correct proportion: The finely dried materials are mixed in exact proportions. The mixing may be done either mechanically or by pneumatic methods(eg. pumped under pressure).
Burning and Grinding: These operations are the same as for the wet process. Except for the mixing of raw materials. In the dry process, the raw materials mixed, fined, and then fed into kiln whereas, in the wet process, the raw materials are crushed separately and then directly mixed in correct proportion in the presence of water to make a fine thin paste known as Slurry.
Must Read Other Powerful Articles
- Properties of Cement
- Types of Cement
- Composition of Cement Clinker
- Hydration of Cement
- Products of Hydration of Cement
- What is Cement?
- Various Tests on Cement
- Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC)
- Manufacturing of Cement By Dry and Wet Process
- Raw Materials of Cement
- History of Cement in Civil Engineering
- Composition of Cement Clinker
- Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC)
- What is Concrete with Definition & History


Thanks, I have been searching for info about this subject matter for ages and yours is the best I have found so far.
Thank u for giving good information
Thank you for uploading
Thanks, Aditya, stay tuned
Thank you
Is the process of manufacturing cement the same as the manufacture of Portland cement
Anane Oliver, All cement procedure are approximate same.