Defintion
A map is a visual drawing of a whole region or some of a locality that’s often shown on a flat surface.
What is Map?
A map’s purpose is to depict precise and elaborated aspects of a particular location, most ordinarily want to show geography. There are many types of maps, together with static, two-dimensional, three-dimensional, dynamic, and interactive maps.
Physical characteristics, Political borders, roads, population, climates, geography, natural resources, and economic activity are all shown on maps.
A map is useful for both a layperson and an informed individual because it consists of a wealth of information. It is as much as the man or woman how he makes use of it. Maps are usually used for: Confirmation, Analysis, Decoration, Investment exploration, Communication, Collection, Hypothesis Stimulation, Control and Planning of Navigation, reading maps, storing information, and analysing and looking back in time.
Because a map should exactly replicate a piece of the earth’s surface, every map must contain a “scale” that specifies the link between the distance on the map and therefore the actual distance on the ground. The map scale is often displayed in a map legend box, besides alternative symbols that provide relevant info concerning the map.
A ratio, often called a depictive fraction, indicates what percentage units ashore correspond to 1 unit on the map. A map with a scale of 1/100000 or 1:100000,
Example:
Tells us that one cm. on the map equals 100000 cm. or 1 km on the ground. The quantitative relation is continuously such that on the map, for example, “one centimetre equals one kilometre,” so on. To read a map effectively symbols, directions, lines, and legends must all be present.
Different Types of Maps
- Political Maps
- Physical Maps
- Thematic Maps
- Topographic Maps
- Climate Maps
- Economic / Resource Maps
- Road Maps
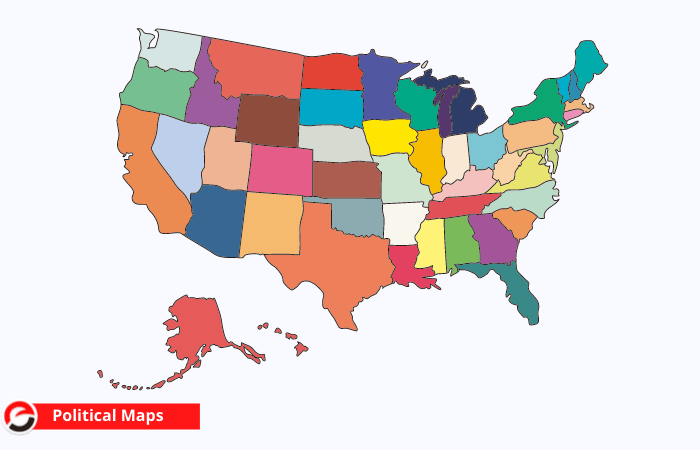
Political Maps
Topographic elements such as mountains aren’t enclosed on a political map. Political map mainly focuses on national and state boundaries. counting on the quality of the maps, these maps additionally give the locations of major and small cities.
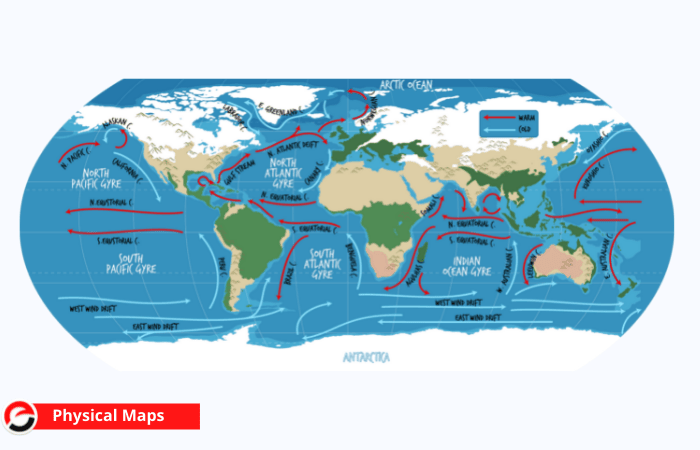
Physical Maps
It depicts a location geographical element. Mountains, rivers, and lakes are commonly pictured on these maps. Blue is wide used to depict bodies of water. Mountains and height variations are sometimes shown in a variety of colours and shades to demonstrate elevation. Greens on physical maps usually represent lower altitudes, whereas browns typically show higher elevations.
Thematic Maps
A thematic map concentrates on a specific theme or issue. These maps differ from the previous six general reference maps therein they show more than merely cities, rivers, political subdivisions, highways, and elevation. If you see these parts on a thematic map, they represent background info that’s utilized as an indicator to boost the topic of the map.

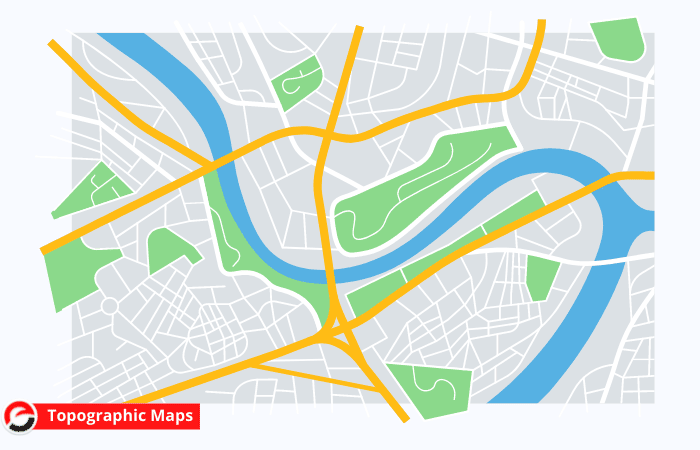
Topographic Maps
A topographic map, like a physical map, depicts several physical terrain aspects. However, not like physical maps, this way of mapping employs contour lines instead of colors to depict changes within the landscape. topographic maps usually have contour lines spread at regular intervals to depict elevation variations (e.g. every line represents a 100-foot elevation change). Approximate lines indicate that the ground is steep.
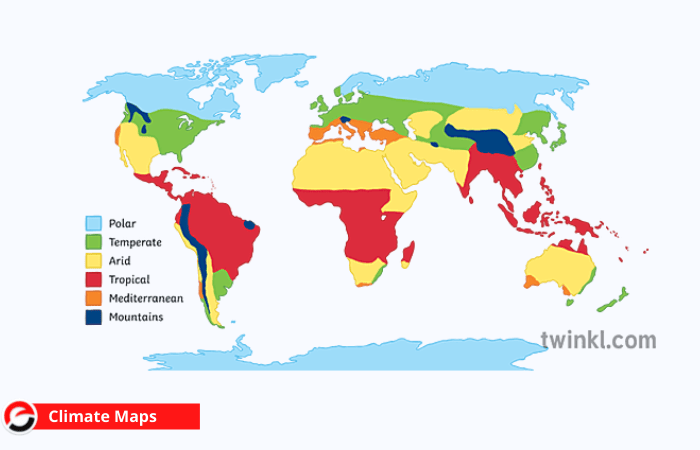
Climate Maps
A climate map depicts info regarding a region’s climate. These maps will show information resembling an area’s distinct climatical zones depending on temperature, the amount of snowfall, or the typical number of overcast days. Color is usually used to depict distinct climate zones on these maps.
Economic / Resource Maps
An economic or resource map depicts the several forms of economic activity or natural resources found in a given region using numerous symbols or colors according to what’s being shown.

Road Maps
A road map is one of the foremost common kinds of maps. These maps depict main and smaller highways and roads, still as airports, cities, and areas of interest like campgrounds, parks, and monuments (depending on the extent of detail). Major highways are often pictured on a map with red lines, broad, while lesser roads are depicted with softer colors and narrower lines.

What is Plan?
The plan is a two-dimensional drawing of a location, area, structure, or building that includes numerous specific information. It also incorporates illustrations and data. It provides extensive information in the symbolic form regarding tiny regions.
Different Types of Plans
- Site Plan
- Floor Plan
- Structural Plan
- Terrace Plan
- Cross-section.
- Elevation
- Landscape plan
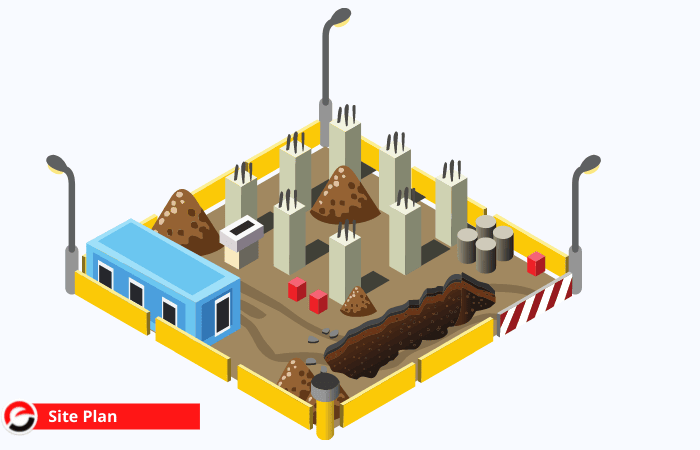
Site Plan
The site plan is the 1st design created for any project and depicts the layout of the development site. site plans offer data on property borders, site access, and existing structures on or close to the construction site, like roads and buildings.
Floor Plan
One of the most important types of building plans is the floor plan. It’s a top-down perspective of a floor plan. Floor plans are a sort of vertical orthographic projection that’s depicted by a plan cut at the window sill level on its floor.

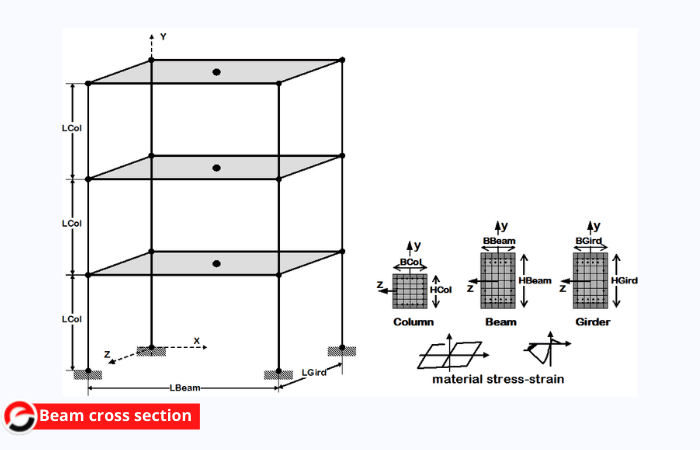
Cross-section Plan
A section plan is a vertical cut section of a building that shows the scale and thickness of any component. merely put, it depicts a sliced image of a building. Section plan consists of
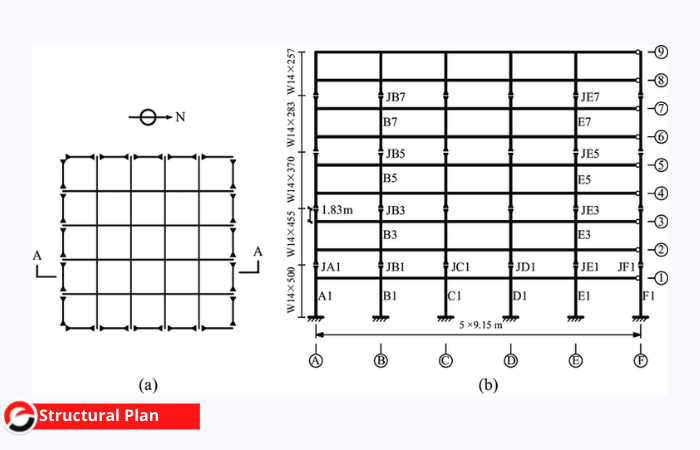
Structural Plan
This sort of plan offers a comprehensive perspective of the building’s structural aspects. The structural design gives details of the size, nomenclature, location, and placement of reinforcement of structural elements and load-carrying elements of the structure. The structural plan is important since it focuses on the structure’s strength.
Terrace Plan
It is the building plan at the roof level. It depicts the stair cabin, lifts cabin (if any), above water tanks, and roof drainage layout. The parapet walls also are enclosed on the terrace layout.

Elevation Plan
An elevation plan sketch is an orthographic projection of one of the building’s side faces. It is a two-dimensional illustration of the building’s facade. The main aim of an elevation sketch is to portray the complete appearance of a certain side of a structure. There are two kinds of elevation plans: External Elevation & Internal Elevation.

Landscape Plan
The landscape plan includes all of the specifics about the flowers, plants, pathways, lawn decorations, fountains, swimming pools (if any), and so on. Well-designed landscaping may improve your living space while also increasing the value of your home. As a result, landscape designs have become one of the most popular forms of construction plans in today’s world.
Difference between map and plan?
|
Map |
Plan |
| A map is a visual drawing of a whole region or some of a locality that’s often shown on a flat surface. | The plan is a two-dimensional drawing of a location, area, structure, or building that includes numerous specific information. It also incorporates illustrations and data.
It provides extensive information in the symbolic form regarding tiny regions. |
| On some map, (topographic specifically) Vertical direction is also shown along with the horizontal and directions. | Plan generally only shows horizontal and direction on it. |
| Normal scale used in the map is 1cm = 100m or more than 100m. | Normal scale used in the plan is 1cm = 10m or less than 10m |
| A map is generally drawn for a large area. | Plan are generally drawn for a small area. |
| Example: – Road map of India etc. | Example: – Plan of a residential bungalow etc. |
Also Read: Blueprint Symbols for Architectural


Leave a comment