Reservoirs are large open storage structure which is used to collect and store water so that it can be drawn and used later for different purposes. It is created by constructing a dam across a river. It is a major component of any water resource project. The reservoir can be used to regulate the natural streamflow and can make the outflow in desired patterns.

Types of Reservoirs
Based on the Purpose of construction of the reservoir, it is classified into four types
1. Storage reservoir
- Since these are used to conserve water they are also called conservation reservoirs
- Storage reservoirs store water in the rainy season and release them when the river flow is low
- In India, these are constructed mainly for irrigation purposes
- Also called single purpose conservation reservoirs

2. Flood Control reservoir
- Mostly called flood-mitigation reservoir
- These are mainly used to store a portion of flood flows to protect the downstream places
- The excess water is stored in the reservoir when the flood discharge exceeds the safe capacity
- The water stored in the reservoir is released when the inflow to the reservoir is decreased
- Designed mostly to moderate the flood and not to conserve water for a long time
- This reservoir has a relatively large, sluice-way capacity for permitting rapid drawdown before or after the occurrence of flood
- There are two types of flood control reservoirs namely Detention reservoirs and Retarding reservoirs.

3. Distribution reservoir
- A reservoir that is constructed within a city water supply system is called a distribution reservoir
- A small storage reservoir to meet the peak demand of water for municipal water supply or irrigation
- Water is pumped at a uniform rate throughout the day for 24 hours but the demand varies from time to time
- It stores water during the lean demand and supplies during the high demand
- Rarely used for the supply of water for irrigation, mainly used for municipal water supply.

4. Multipurpose reservoirs
- Constructed to serve for more than one purpose
- For example – Irrigation, Hydroelectric power, water supply, navigation, flood control, recreation, and wildlife conservation
- The projects having reservoirs that are designed and operated to serve two or more purposes should be termed multipurpose.

Purpose of reservoirs
The main purposes of reservoirs are
- Used to meet the water requirements of cities during dry weather flow in rivers
- For hydroelectric power generation during the months of discharge in the ring to maintain a minimum water level
- For the protection of low lying areas against flooding
- For growing fishes and other aquatic life
- For recreation purposes such as swimming etc.
- To meet the irrigation water requirements of the area when discharge in a river is lower than the demand
- To protect the hydroelectric equipment and pumping machinery from silt and debris present in the water.
Advantages of reservoirs
- Controlled and sustained supply of water for irrigation encourages to use of additional areas for cropping
- After proper treatment water can be used for drinking purposes
- The water stored can be used to generate electricity
- Can be used for flood control
- Upstream water ponds can be used for fish farming
- Control the debris from the water.
Disadvantages of reservoirs
- A large area of land will be submerged and will be turned into a reservoir by the rise of water
- Many people should have to be relocated
- Life cycles of the aquatic animals will get affected
- On the downstream side, there will be a decrease in the nutrients
- Overall there will be a reduction in diversity around the reservoir.
Difference between dams and reservoirs
| Dams | Reservoirs |
| It is a wall constructed across a river | It is formed by the water that is accumulated behind the dam |
| Water is stored behind the dam | Water forms the reservoir |
| Displaces and obstructs the migration of fishes and affects other aquatic life | Displaces and affects the people which are living in the area |
| Dams are used to create sites for hydroelectric generation and improve living standards among people | Provides enough water for consumption and also stores water if available in excess |
| Provides a site for tourist attraction | Water transportation is provided |
| Looks like a concrete structure wall | Looks like a water body like a river or a lake |
Impact of reservoirs on environment
- The construction of reservoirs mainly affects aquatic life and also disrupts the life cycles of fish
- It causes the dislocation of the people living near that place
- The quality of life may get affected due to the storage of water.
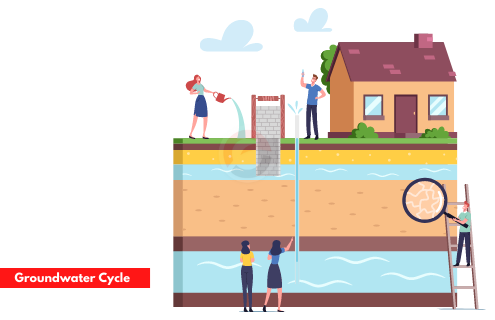
How does nature maintain groundwater reservoirs?
The groundwater reservoir is maintained by the water that percolates into the rock layer of the ground from natural discharges, the discharge will be mainly from the precipitation. The water from precipitation seeps into the ground and leads to underground reservoirs.
List of reservoirs in India
There is a total of 44 reservoirs, please check the list with the river name.
| Reservoir | River Name | |
| 1 | Tatipudi Reservoir Project | Gosthani River |
| 2 | Gandipalem Reservoir | Manneru River |
| 3 | Gobind Sagar Reservoir | Sutlej River |
| 4 | Maharana Pratap Sagar Reservoir | Pong Dam Lake |
| 5 | Salal Project | Chenab River |
| 6 | Chutak Hydroelectric Project | |
| 7 | Ghataprabha Reservoir | Ghataprabha River |
| 8 | Hemavathi Reservoir | Hemavati River |
| 9 | Tawa Reservoir | Tawa River |
| 10 | Indirasagar Project | Narmada River |
| 11 | Narmada Dam Project | Narmada River |
| 12 | Balimela Reservoir | Sileru River |
| 13 | Aliyar Reservoir | Aliyar River |
| 14 | Chittar Reservoir | Chittar River |
| 15 | Krishnagiri Reservoir | Thenpennai River |
| 16 | Manimuthar Reservoir | Tamirabarani River |
| 17 | Pechiparai Reservoir | Kodayar River |
| 18 | Shoolagiri Chinnar Reservoir | Chinnar River |
| 19 | Thunakadavu Reservoir | Thunacadavu River |
| 20 | Varattu Pallam Reservoir | |
| 21 | Vidur Reservoir | |
| 22 | Amaravathi Reservoir | Amaravathi River |
| 23 | Gundar Reservoir | Berijam Lake |
| 24 | Kullursandai Reservoir | Arjuna Nadi |
| 25 | Pambar Reservoir | Pambar River |
| 26 | Periyar Reservoir | Periyar River |
| 27 | Stanley Reservoir | Kaveri River |
| 28 | Uppar Reservoir | |
| 29 | Vattamalaikarai Odai Reservoir | Odai River |
| 30 | Willingdon Reservoir | Periya Odai River |
| 31 | Bhavanisagar Reservoir | Bhavani River |
| 32 | Kodaganar Reservoir | Kodagananar River |
| 33 | Manimukthanadhi Reservoir | |
| 34 | Parambikulam Reservoir | Parambikulam River |
| 35 | Sholayar Reservoir | |
| 36 | Thirumurthi Reservoir | Parmabikulam and Aliyar River |
| 37 | Varadamanadhi Reservoir | |
| 38 | Vembakottai Reservoir | Vaippar River |
| 39 | Manjalar Reservoir | |
| 40 | Dindi Reservoir | Krishna River |
| 41 | Lower Manair Reservoir | Manair River |
| 42 | Himayat Sagar Reservoir | Osman Sagar |
| 43 | Shriram Sagar Reservoir | Godavari River |
| 44 | Rihand Project | Rihand River and Son River |
Also Read: Sardar Sarovar dam and List of Dams in India
Question and Answers
Underground reservoirs of freshwater are called__________?
Groundwater is called the underground reservoirs of freshwater.
Types of reservoirs in India
There are three types of reservoirs in India
• Large reservoirs ( covers an area of 5000 and more hectares)
• Medium reservoirs (Covering an area of 1000 – 5000 hectares)
• Small reservoirs (Covering an area less than 1000 hectares)
Names of water reservoirs in Karnataka
Ghataprabha and Hemavathi Reservoirs are the two reservoirs in Karnataka.
What is the range of temperature at hydrothermal reservoirs?
The hydrothermal reservoirs are at moderate depth containing steam and hot water under pressure. These are maintained at a temperature of about 350°C.
Top 10 reservoirs in India
1. Dindi Reservoir
2. Lower Manair Reservoir
3. Tatipudi Reservoir Project
4. Gandipalem Reservoir
5. Himayat Sagar Reservoir
6. Shriram Sagar Reservoir
7. Gobind Sagar Reservoir
8. Maharana Pratap Sagar Reservoir
9. Ghataprabha Reservoir
10. Hemavathi Reservoir
Why are dams and reservoirs built?
Dams and reservoirs are built to store and distribute water for different purposes. Mainly for distributing and supplying it in a controlled manner. Water can be used for various purposes like irrigation, hydroelectricity, water supply using dams and reservoirs.


Leave a comment