What is Tube Well?
A tube well is a particular kind of deep well that draws water from the earth’s crust. It can pull out water from one or more constrained aquifers. It is a tube that is buried under the ground. Slotted portions of the tube contain the level with limited aquifers. It also has hollow pipes. These pipes are without slots with impervious layers.

Blind pies are hollow and do not have any slots on their surface. Strainer pipes or perforated pipes are used to describe the pipe components. They have slots on their surface. Thus, strainer pipes and blind pipes both make up a tube well. These strainers come in a variety of forms.
Also Read: Rainwater Harvesting System
Materials used to construct Tube Wells
- Zinc free brass
- Stainless steel
- Low carbon steel
- High copper alloy
Types of tube wells
1. Cavity Tube well
This type of tube well has an underground pipe. Also, others are on the base of a thick layer of clay in a cavity-type tube well. It doesn’t use strainers; so it gets its supplies from the bottom. In the early phases of pumping, fine sand and water are released. This causes a space to form at the bottom.
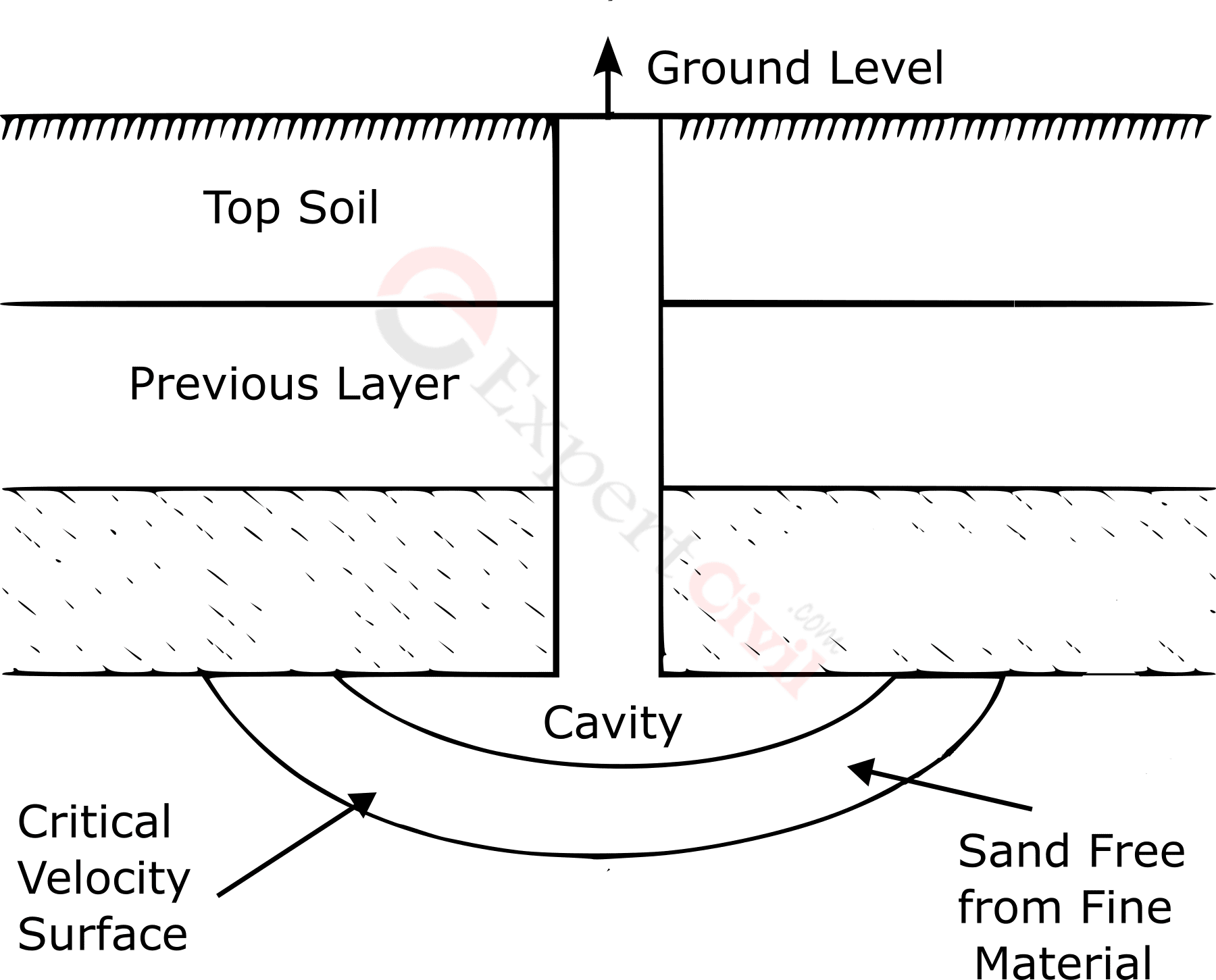
Aquifer water enters the well pipe through the cavity. As the pumping process continues, the cavity’s spherical area expands outward. Then the water flow becomes slow. As a result, it prevents sand particles from entering the well pipe. A cavity-type tube well initially produces sandy water. Then, clear water is produced after clearing lime. This tubewell extracted water from the bottom. It can only access one specific aquifer. Thus, a cavity-type tube well is comparable to a deep open well. In a cavity-type tube well, the area of the flow section is increased by enlarging the cavity. The hollow is created by a particular discharge type.
What Is Cavity Formation In Wells?
The cavity is formed in open wells to form some extent of cementation. The formation of a cavity below the bottom of a shallow well is dangerous. It may cause cracks in the well lining. That’s why the water at high velocity can be withdrawn from wells is constrained. In the case of deep wells, water at maximum rate can be released in a particular direction
2. Slotted Tube well
A slotted type tube well is plain for the majority of its length and slotted at one end. The pipe that enters the confined aquifer is 5 meters in length. The slots measure 25 mm x 3 mm and are spaced 10 to 12 mm apart. A combination of gravel and coarse sand surrounds the well tubing.
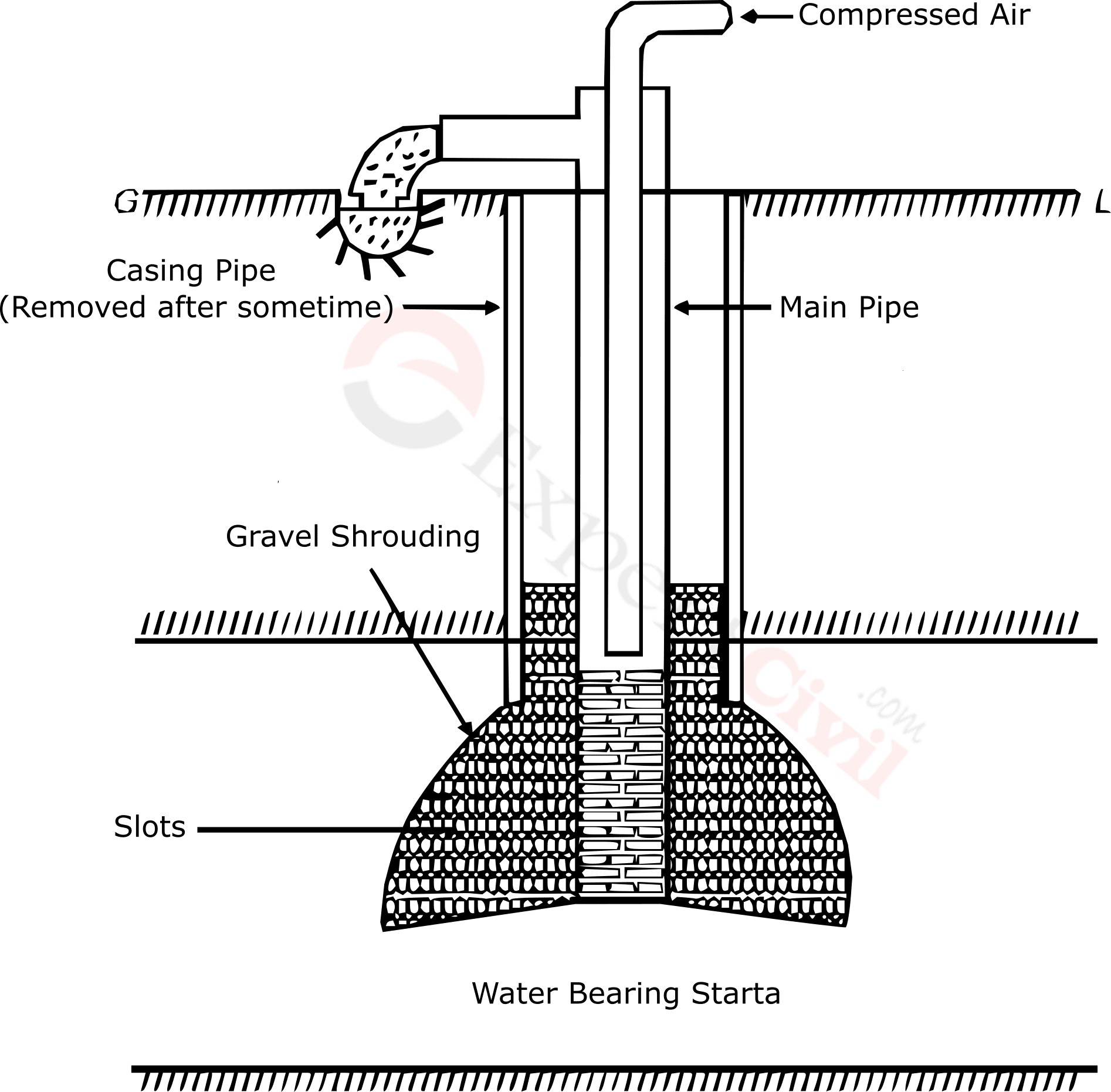
It can stop the fine sand particles from entering (bajri). Before removing the casing pipe, a combination of gravel and gritty sand is poured from the top. This mixture is added into the annular space between the well pipe and the pipe. The shrouding must be present in the slotted portion of well pipe.
3. Strainer Tube Well
This tube well consists of blind pipes and strainer pipes. This tube well is generally unsuitable for a very fine sandy layer. In this situation, screen openings are likely to choke easily. It is the most widely used type of tube well in developing countries. It is so common that whenever we talk about a tube well, we are referring to a strainer-type tube well.

The casing pipe is 5 to 10 cm greater in diameter than the well pipe used to bore the hole. A bore hole of 20 to 25 cm in diameter is needed for a well. The well pipe consists of the strainer and blind pipes. It is lowered into the borehole. Blind and strainer pipe lengths are adjusted. So, they run up against impermeable strata and water-bearing aquifers. The well is often filled at the bottom with cement concrete. A short blind pipe helps to allow the settlement of sand particles. Then, they passed through the strainer.
Types of Strainers:
Some of the common types of strainers used for the tube wells are as follows:
- Cook strainer
- Tej strainer
- Brownlie strainer
- Ashford strainer
- Leggett strainer
- Phoenix strainer
- Layne and Bowler strainer.
Also Read: What is Aquifuge, Aquifer, Aquiclude and Aquitard in Geological Formations
What is the difference between a strainer and a slotted type well?
| Slotted Tubewell | Strainer Tubewell |
| i) In a slotted type tube well, the gravel and coarse sand prevent the fine particles. They don’t send shrouding to enter the well pipe. | i) In contrast to a strainer-type tube well, the pipes are surrounded by wire mesh. |
| ii) A slotted type tube well can only tap one restricted aquifer | ii) A strainer-type tube well can tap one or more confined aquifers laying on one another. |
| iii) A strainer-type tube well has a specific depth of 75 to 100 m. | iii) Slotted type of well is available with one stratum. |
| iv) It cannot be built if sufficient water carrying level is not up to the mark. | iv) It can contain a significant amount of water in it. |
Conclusion:
In short, this article is all about what tube well is and its common types. Each term is fully explained to quench your queries. I hope you get enough information by reading this article.
Also Read: Different Types of Dam


Leave a comment