Various tests on cement
Basically, two types of tests are undertaken for assessing the quality of cement. These are either field tests or lab tests. The current section describes these tests in details lets know more about ‘ Various Tests on Cement ‘.

Field test of cement
There are four field tests that may be carried out to ascertain roughly the quality of cement. There are four types of field tests to access the colour, physical property, and strength of the cement as described below.
Colour
- The colour of cement should be uniform.
- It should be typical cement colour i.e. grey colour with a light greenish shade.
Physical properties
- Cement should feel smooth when touched between fingers.
- If the hand is inserted in a bag or heap of cement, it should feel cool.
Presence of lumps
- Cement should be free from lumps.
- For moisture content of about 5 to 8%, this increase of volume may be much as 20 to 40 %, depending upon the grading of sand.

Strength
- A thick paste of cement with water is made on a piece of thick glass and it is kept underwater for 24 hours. It should set and not crack.
Laboratory tests:
Six laboratory tests are conducted mainly for assessing the quality of cement. These are:
- Fineness,
- Compressive Strength
- Consistency
- Setting Time
- Soundness
- Tensile Strength
Fineness Test
- This test is carried out to check the proper grinding of cement.
- The fineness of cement particles may be determined either by the sieve test or permeability apparatus test.
- In the sieve test, the cement weighing 100 gm is taken and it is continuously passed for 15 minutes through standard BIS sieve no. 9.
- The residue is then weighed and this weight should not be more than 10% of the original weight.
- In the permeability apparatus test, a specific area of cement particles is calculated. This test is better than the sieve test. The specific surface acts as a measure of the frequency of particles of average size.

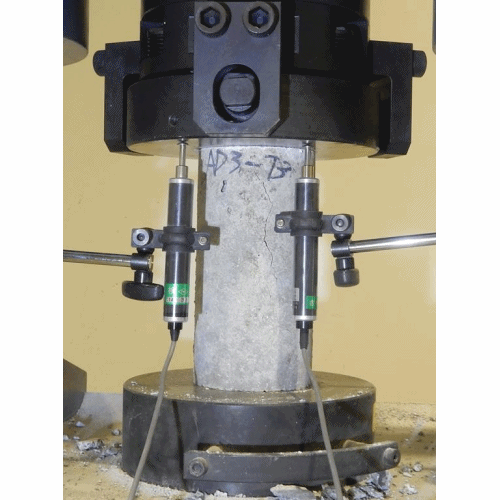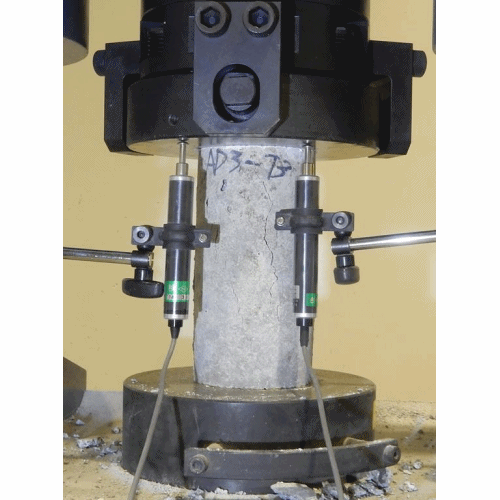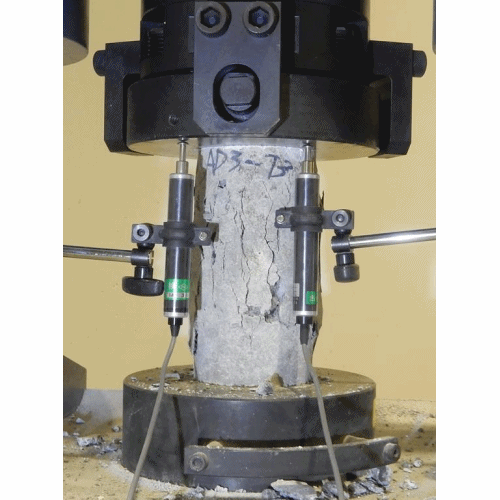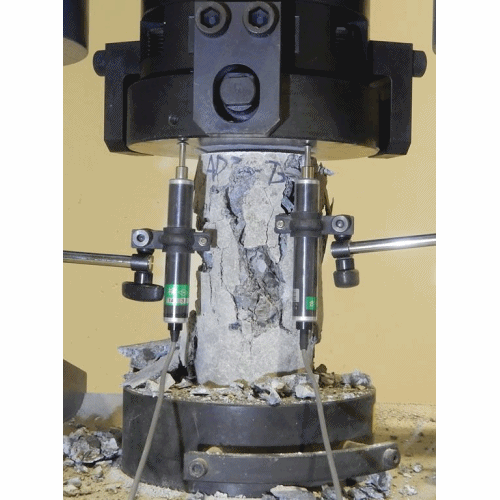
Compressive Strength Test
- This test is carried out to determine the compressive strength of cement.
- The mortar of cement and sand is prepared in ratio of 1:3.
- Water is added to mortar in water-cement ratio 0.4.
- The mortar is placed in moulds. The test specimens are in the form of cubes and the moulds are of metals. For 70.6 mm and 76 mm cubes, the cement required is 185gm and 235 gm respectively.
- Then the mortar is compacted in a vibrating machine for 2 minutes and the moulds are placed in a damp cabin for 24 hours.
- The specimens are removed from the moulds and they are submerged in clean water for curing.
- The cubes are then tested in a compression testing machine at the end of 3days and 7 days. Thus compressive strength was found out.
Consistency Test
- The purpose of this test is to determine the percentage of water required for preparing cement pastes for other tests.
- Take 300 gm of cement and add 30 per cent by weight or 90 gm of water to it.
- Mix water and cement thoroughly.
- Fill the mould of the Vicat apparatus and the gauging time should be 3.75 to 4.25 minutes.
- Vicat apparatus consists of a needle is attached to a movable rod with an indicator attached to it.
- There are three attachments: square needle, plunger, and needle with annular collar.
- The plunger is attached to the movable rod. the plunger is gently lowered on the paste in the mould.
- The settlement of the plunger is noted. If the penetration is between 5 mm to 7 mm from the bottom of the mould, the water added is correct. If not the process is repeated with different percentages of water till the desired penetration is obtained.

Setting time
- This test is used to detect the deterioration of cement due to storage. The test is performed to find out the initial setting time and final setting time.
- Cement mixed with water and cement paste is filled in the Vicat mould.
- The square needle is attached to the moving rod of the Vicat apparatus.
- The needle is quickly released and it is allowed to penetrate the cement paste. In the beginning, the needle penetrates completely. The procedure is repeated at regular intervals until the needle does not penetrate completely. (up to 5mm from bottom)
- Initial setting time =<30min for ordinary Portland cement and 60 min for low heat cement.
- The cement paste is prepared as above and it is filled in the Vicat mould.
- The needle with the annular collar is attached to the moving rod of the Vicat apparatus.
- The needle is gently released. The time at which the needle makes an impression on the test block and the collar fails to do so is noted.
- Final setting time is the difference between the time at which water was added to cement and time as recorded in the previous step, and it is =<10 hours.
Soundness Test
- The purpose of this test is to detect the presence of uncombined lime in the cement.
- The cement paste is prepared.
- The mould is placed and it is filled by cement paste.
- It is covered at the top by another glass plate. A small weight is placed at the top and the whole assembly is submerged in water for 24 hours.
- The distance between the points of the indicator is noted. The mould is again placed in water and heat is applied in such a way that boiling point of water is reached in about 30 minutes. The boiling of water is continued for one hour.
- The mould is removed from the water and it is allowed to cool down.
- The distance between the points of the indicator is again measured. The difference between the two readings indicates the expansion of cement and it should not exceed 10 mm.

Tensile strength Test
- This test was formerly used to have an indirect indication of the compressive strength of cement.
- The mortar of sand and cement is prepared.
- The water is added to the mortar.
- The mortar is placed in briquette moulds. The mould is filled with mortar and then a small heap of mortar is formed at its top. It is beaten down by a standard spatula till water appears on the surface. The same procedure is repeated for the other face of the briquette.
- The briquettes are kept in a damp for 24 hours and carefully removed from the moulds.
- The briquettes are tested in a testing machine at the end of 3 and 7 days and the average is found out.

Must Read Other Powerful Articles
- Types of Cement
- Composition of Cement Clinker
- Hydration of Cement
- Products of Hydration of Cement
- What is Cement?
- Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC)
- Manufacturing of Cement By Dry and Wet Process
- Raw Materials of Cement
- History of Cement in Civil Engineering
- Composition of Cement Clinker
- Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC)
- What is Concrete with Definition & History


Leave a comment