A building either residential, commercial, or multi-story building, the stair is definite or precise arrangements that give or provide us access from one floor to another floor or to each floor of a building.
In other words, It is an arrangement provided for vertical movement of people residing or living in any building.
What is Stairs?
A well-planned and designed arrangement of a number of steps provided in a building for vertical movement of people is called stairs.
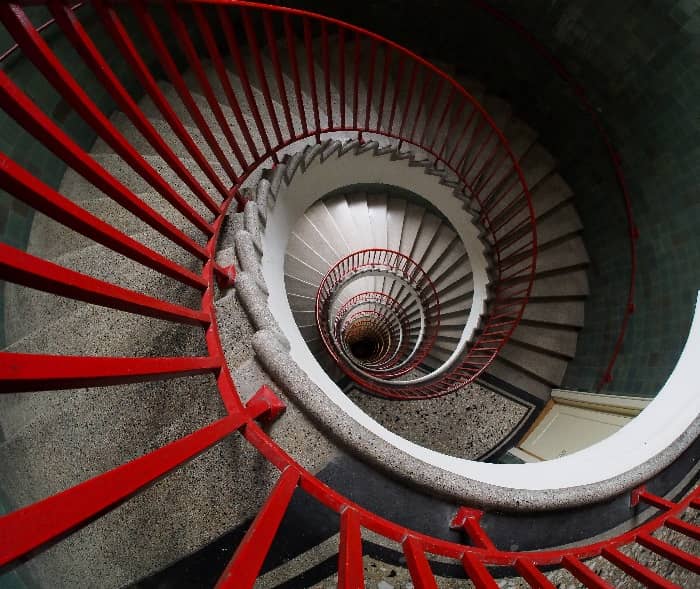

Stairs
Stairs may be made from bricks, stone, steel, plain cement concrete, reinforced cement concrete, wooden, or timber.
What is Staircase?
Space provided in the building for the stairs is called the staircase.

Spiral Staircase
Requirements of Staircase
- Give an entrance starting with one floor then onto the next floor
- Provide a safe movement between floors.
- Provide a simple means of movement between floors.
- Provide a reasonable method for getting out in the event of a fire.
- Provide a means of establishing fittings and furniture between floor levels.
Components of Staircase

Components of Staircase
- Scotia- It is a three-sided wooden block utilized between the nosing to give it extra strength.
- String- A inclined part that holds or supports the steps is known as a String. The strings are given on each side of steps, or in the focal point of steps as a help to the means.
- Riser- The vertical portion which is in the front is called a riser.
- Flight- A number of continuous steps between two floors or one landing to landing or one floor to landing are called flight.
- Step- The structural part which consists of tread and riser is called step.
- Hand Rail- The inclined member which is for handholding or safeguard for a person and connected from the vertical baluster which holds it up for stairs that are open from one side.
- Headroom- The distance between the slope lime and the adjoining of the tread to the other floor is called headroom and it should not be less than 2.20m.
- Landing- A horizontal part or platform which is between two risers that serve as rest for the foot is called landing. It also provides turning for another step or another floor.
- Nosing- The outer edge of the tread is called nosing.
- Baluster- The vertical member provided between the steps to hold the hand drill is called balusters.
- Run- The horizontal part of the staircase which is used for placing the foot is called run or tread.
- Going- The horizontal surface which is between the first and last riser. It should not be less than 220mm.
- Soffit- The inclined surface under a flight of stairs is called the soffit.
- Tread- The horizontal part of the staircase which is used for placing the foot is called run or tread.
- Balustrade- The combination of balusters or handrails is called balustrade.
Also Read: All you need to know about Skirting Tiles
Types of Staircase
1. Straight Stairs
The straight staircase rises from one to another floor without any turning or intermediate. It is also called cottage stairs. The most economical way of using a straight staircase is the centre of a building for going and returning back.

Straight Stairs
a. Turning Stairs
The turning stairs have an opening between the front and back flights. The change in direction is directed from the centre between flights and winders. There are many types of turning staircases as follows.
b. Quarter Turn Stairs
Quarter turn stair is that type of stair when the flight is directed or turned by 90 degrees. It is usually provided to change its direction to the left or right.

Quarter Turn Stairs
This can be also achieved by starting a space landing, there are classified as follows:
- Newel Quarter Turn Staircase: these stairs have the new posts at the starting and the end of end flight. Quarter turn may be landing or winders.
Newel Quarter Turn Staircase
- Geometrical Quarter Turn Staircase: there is no continuous handrail with no new position on the landing.

Geometrical Quarter Turn Stair
2. Half Fold Stairs
Half fold stair is directed or changed to 180 degrees, these are classified into many types as follows:-
a. Dog-legged Stairs
A dog-leg is a distribution of stairs between two floors of a building, often a domestic building, in which a flight of stairs rises to a half-landing before turning at a right angle and continuing upwards.
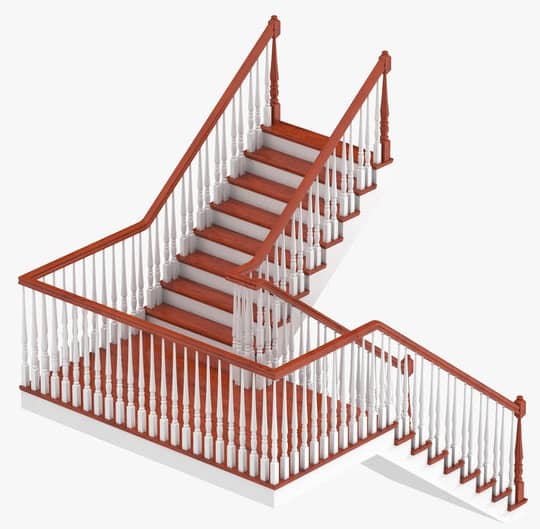

Dog-legged Stair
b. Open New Half-turn Stairs
c. Geometrical Half-fold Stairs
3. Three Quarter Turn Stairs
This type of stair is used when the dimension of the staircase room is restricted and the vertical distance between the two floors is sufficient.
4. Bifurcated Stairs
the stair in which the width of the more on the wall which is subdivided into narrow flight at the mid landing. This is very common in public buildings and two narrow flights start at the entrance on centre landing.

Bifurcated Stairs
5. Circular Stairs
the stair when it is viewed from the top looks like a circular stair with a centre of curvature and a large radius.

Circular Stairs
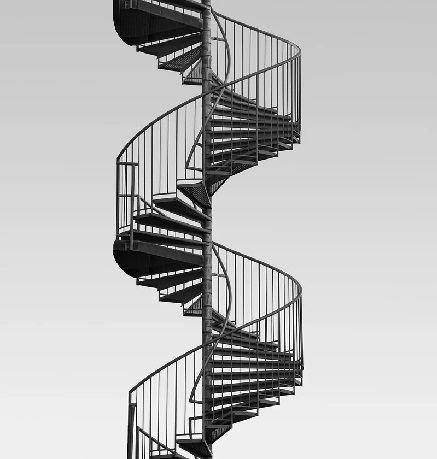
6. Spiral Stairs
The spiral stair is quite similar to a circular staircase but the radius is small and the handrill of the staircase supports the middle part.

Spiral Stairs
Spiral Stair stairs may be constructed from the following materials:
- Cast iron
- Mild steel
- Concrete
- Timber
- Precast concrete
- Cast in-situ
- Metal
- Stone
Also Read: Types of buildings
Requirements for Good Staircase
Some of the important points should be kept in mind while providing or designing stair are as follows:
- Location: It should be easily accessible to all the parts of the building and located there where sufficient light and proper ventilation is available.
- Width of stairs: The width of the stairs depending on the requirements of the building. The average width of the residential building must be 1m and for public buildings, it should be 1.5m to 2m
- Length of Flight: Maximum number of steps is provided for comfortable access to the floor by steps and the maximum number of steps is 12 and minimum of 3.
- Pitch of stairs: The pitch of the stair must not exceed 40° and minimum of 25°
- Landing: The width of the landing should not be less than the width of the stair.
- Headroom: The distance between the slope line and the adjoining of the tread to the other floor is called headroom and it should not be less than 2.20m.
- Handrails: It must be provided with the minimum height of 100 cm from the centre of the tread.
- Winders: the winders should be avoided or they should be provided at the lower end of the flight.
- Materials: the material from which the stair is constructed must be fire-resistant. The strength must be good enough to withstand.
- Step proportions: The ratio or proportion of the going and rise of a stair must be ideal for comfortable access of the people while moving from one floor to the next.
These are the general experimental rule for the ideal proportional follows:-

parts of staircase
- Treads in cm + 2(rise in cm)= 60
- Treads in cm + (rise in cm)= 400 to 450 approx
- Treads in cm + (rise in cm)= 40 to 45 approx
- Standard sizes = Tread 30 cm, Rise 14 cm
Generally, sizes of steps are:
- Public buildings: (27 cm X 15 cm) to (30 X 14 cm)
- Residential buildings: 25 cm X 16 cm.
Also Read: 11 Steps in Construction of Multi Storey Buildings



Leave a comment